// Copyright 2014 The Flutter Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file.
import 'dart:math' as math;
import 'dart:ui' as ui;
import 'dart:ui' show Brightness;
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'basic.dart';
import 'debug.dart';
import 'framework.dart';
/// Whether in portrait or landscape.
enum Orientation {
/// Taller than wide.
portrait,
/// Wider than tall.
landscape
}
/// Information about a piece of media (e.g., a window).
///
/// For example, the [MediaQueryData.size] property contains the width and
/// height of the current window.
///
/// To obtain the current [MediaQueryData] for a given [BuildContext], use the
/// [MediaQuery.of] function. For example, to obtain the size of the current
/// window, use `MediaQuery.of(context).size`.
///
/// If no [MediaQuery] is in scope then the [MediaQuery.of] method will throw an
/// exception. Alternatively, [MediaQuery.maybeOf] may be used, which returns
/// null instead of throwing if no [MediaQuery] is in scope.
///
/// ## Insets and Padding
///
/// 
///
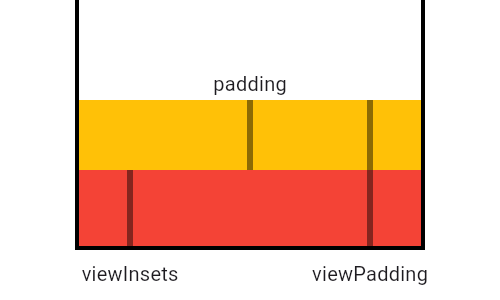
/// This diagram illustrates how [padding] relates to [viewPadding] and
/// [viewInsets], shown here in its simplest configuration, as the difference
/// between the two. In cases when the viewInsets exceed the viewPadding, like
/// when a software keyboard is shown below, padding goes to zero rather than a
/// negative value. Therefore, padding is calculated by taking
/// `max(0.0, viewPadding - viewInsets)`.
///
/// {@animation 300 300 https://flutter.github.io/assets-for-api-docs/assets/widgets/window_padding.mp4}
///
/// In this diagram, the black areas represent system UI that the app cannot
/// draw over. The red area represents view padding that the application may not
/// be able to detect gestures in and may not want to draw in. The grey area
/// represents the system keyboard, which can cover over the bottom view padding
/// when visible.
///
/// MediaQueryData includes three [EdgeInsets] values:
/// [padding], [viewPadding], and [viewInsets]. These values reflect the
/// configuration of the device and are used and optionally consumed by widgets
/// that position content within these insets. The padding value defines areas
/// that might not be completely visible, like the display "notch" on the iPhone
/// X. The viewInsets value defines areas that aren't visible at all, typically
/// because they're obscured by the device's keyboard. Similar to viewInsets,
/// viewPadding does not differentiate padding in areas that may be obscured.
/// For example, by using the viewPadding property, padding would defer to the
/// iPhone "safe area" regardless of whether a keyboard is showing.
///
/// The viewInsets and viewPadding are independent values, they're
/// measured from the edges of the MediaQuery widget's bounds. Together they
/// inform the [padding] property. The bounds of the top level MediaQuery
/// created by [WidgetsApp] are the same as the window that contains the app.
///
/// Widgets whose layouts consume space defined by [viewInsets], [viewPadding],
/// or [padding] should enclose their children in secondary MediaQuery
/// widgets that reduce those properties by the same amount.
/// The [removePadding], [removeViewPadding], and [removeViewInsets] methods are
/// useful for this.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [Scaffold], [SafeArea], [CupertinoTabScaffold], and
/// [CupertinoPageScaffold], all of which are informed by [padding],
/// [viewPadding], and [viewInsets].
@immutable
class MediaQueryData {
/// Creates data for a media query with explicit values.
///
/// Consider using [MediaQueryData.fromWindow] to create data based on a
/// [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher].
const MediaQueryData({
this.size = Size.zero,
this.devicePixelRatio = 1.0,
this.textScaleFactor = 1.0,
this.platformBrightness = Brightness.light,
this.padding = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.viewInsets = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.systemGestureInsets = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.viewPadding = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.alwaysUse24HourFormat = false,
this.accessibleNavigation = false,
this.invertColors = false,
this.highContrast = false,
this.disableAnimations = false,
this.boldText = false,
this.navigationMode = NavigationMode.traditional,
}) : assert(size != null),
assert(devicePixelRatio != null),
assert(textScaleFactor != null),
assert(platformBrightness != null),
assert(padding != null),
assert(viewInsets != null),
assert(systemGestureInsets != null),
assert(viewPadding != null),
assert(alwaysUse24HourFormat != null),
assert(accessibleNavigation != null),
assert(invertColors != null),
assert(highContrast != null),
assert(disableAnimations != null),
assert(boldText != null),
assert(navigationMode != null);
/// Creates data for a media query based on the given window.
///
/// If you use this, you should ensure that you also register for
/// notifications so that you can update your [MediaQueryData] when the
/// window's metrics change. For example, see
/// [WidgetsBindingObserver.didChangeMetrics] or
/// [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.onMetricsChanged].
MediaQueryData.fromWindow(ui.SingletonFlutterWindow window)
: size = window.physicalSize / window.devicePixelRatio,
devicePixelRatio = window.devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor = window.textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness = window.platformBrightness,
padding = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.padding, window.devicePixelRatio),
viewPadding = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.viewPadding, window.devicePixelRatio),
viewInsets = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.viewInsets, window.devicePixelRatio),
systemGestureInsets = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.systemGestureInsets, window.devicePixelRatio),
accessibleNavigation = window.accessibilityFeatures.accessibleNavigation,
invertColors = window.accessibilityFeatures.invertColors,
disableAnimations = window.accessibilityFeatures.disableAnimations,
boldText = window.accessibilityFeatures.boldText,
highContrast = window.accessibilityFeatures.highContrast,
alwaysUse24HourFormat = window.alwaysUse24HourFormat,
navigationMode = NavigationMode.traditional;
/// The size of the media in logical pixels (e.g, the size of the screen).
///
/// Logical pixels are roughly the same visual size across devices. Physical
/// pixels are the size of the actual hardware pixels on the device. The
/// number of physical pixels per logical pixel is described by the
/// [devicePixelRatio].
final Size size;
/// The number of device pixels for each logical pixel. This number might not
/// be a power of two. Indeed, it might not even be an integer. For example,
/// the Nexus 6 has a device pixel ratio of 3.5.
final double devicePixelRatio;
/// The number of font pixels for each logical pixel.
///
/// For example, if the text scale factor is 1.5, text will be 50% larger than
/// the specified font size.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.textScaleFactorOf], a convenience method which returns the
/// textScaleFactor defined for a [BuildContext].
final double textScaleFactor;
/// The current brightness mode of the host platform.
///
/// For example, starting in Android Pie, battery saver mode asks all apps to
/// render in a "dark mode".
///
/// Not all platforms necessarily support a concept of brightness mode. Those
/// platforms will report [Brightness.light] in this property.
final Brightness platformBrightness;
/// The parts of the display that are completely obscured by system UI,
/// typically by the device's keyboard.
///
/// When a mobile device's keyboard is visible `viewInsets.bottom`
/// corresponds to the top of the keyboard.
///
/// This value is independent of the [padding] and [viewPadding]. viewPadding
/// is measured from the edges of the [MediaQuery] widget's bounds. Padding is
/// calculated based on the viewPadding and viewInsets. The bounds of the top
/// level MediaQuery created by [WidgetsApp] are the same as the window
/// (often the mobile device screen) that contains the app.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ui.window], which provides some additional detail about this property
/// and how it relates to [padding] and [viewPadding].
final EdgeInsets viewInsets;
/// The parts of the display that are partially obscured by system UI,
/// typically by the hardware display "notches" or the system status bar.
///
/// If you consumed this padding (e.g. by building a widget that envelops or
/// accounts for this padding in its layout in such a way that children are
/// no longer exposed to this padding), you should remove this padding
/// for subsequent descendants in the widget tree by inserting a new
/// [MediaQuery] widget using the [MediaQuery.removePadding] factory.
///
/// Padding is derived from the values of [viewInsets] and [viewPadding].
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ui.window], which provides some additional detail about this
/// property and how it relates to [viewInsets] and [viewPadding].
/// * [SafeArea], a widget that consumes this padding with a [Padding] widget
/// and automatically removes it from the [MediaQuery] for its child.
final EdgeInsets padding;
/// The parts of the display that are partially obscured by system UI,
/// typically by the hardware display "notches" or the system status bar.
///
/// This value remains the same regardless of whether the system is reporting
/// other obstructions in the same physical area of the screen. For example, a
/// software keyboard on the bottom of the screen that may cover and consume
/// the same area that requires bottom padding will not affect this value.
///
/// This value is independent of the [padding] and [viewInsets]: their values
/// are measured from the edges of the [MediaQuery] widget's bounds. The
/// bounds of the top level MediaQuery created by [WidgetsApp] are the
/// same as the window that contains the app. On mobile devices, this will
/// typically be the full screen.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ui.window], which provides some additional detail about this
/// property and how it relates to [padding] and [viewInsets].
final EdgeInsets viewPadding;
/// The areas along the edges of the display where the system consumes
/// certain input events and blocks delivery of those events to the app.
///
/// Starting with Android Q, simple swipe gestures that start within the
/// [systemGestureInsets] areas are used by the system for page navigation
/// and may not be delivered to the app. Taps and swipe gestures that begin
/// with a long-press are delivered to the app, but simple press-drag-release
/// swipe gestures which begin within the area defined by [systemGestureInsets]
/// may not be.
///
/// Apps should avoid locating gesture detectors within the system gesture
/// insets area. Apps should feel free to put visual elements within
/// this area.
///
/// This property is currently only expected to be set to a non-default value
/// on Android starting with version Q.
///
/// {@tool dartpad --template=stateful_widget_material}
///
/// For apps that might be deployed on Android Q devices with full gesture
/// navigation enabled, use [systemGestureInsets] with [Padding]
/// to avoid having the left and right edges of the [Slider] from appearing
/// within the area reserved for system gesture navigation.
///
/// By default, [Slider]s expand to fill the available width. So, we pad the
/// left and right sides.
///
/// ```dart
/// double _currentValue = 0.2;
///
/// @override
/// Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// EdgeInsets systemGestureInsets = MediaQuery.of(context).systemGestureInsets;
/// return Scaffold(
/// appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Pad Slider to avoid systemGestureInsets')),
/// body: Padding(
/// padding: EdgeInsets.only( // only left and right padding are needed here
/// left: systemGestureInsets.left,
/// right: systemGestureInsets.right,
/// ),
/// child: Slider(
/// value: _currentValue.toDouble(),
/// onChanged: (double newValue) {
/// setState(() {
/// _currentValue = newValue;
/// });
/// },
/// ),
/// ),
/// );
/// }
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
final EdgeInsets systemGestureInsets;
/// Whether to use 24-hour format when formatting time.
///
/// The behavior of this flag is different across platforms:
///
/// - On Android this flag is reported directly from the user settings called
/// "Use 24-hour format". It applies to any locale used by the application,
/// whether it is the system-wide locale, or the custom locale set by the
/// application.
/// - On iOS this flag is set to true when the user setting called "24-Hour
/// Time" is set or the system-wide locale's default uses 24-hour
/// formatting.
final bool alwaysUse24HourFormat;
/// Whether the user is using an accessibility service like TalkBack or
/// VoiceOver to interact with the application.
///
/// When this setting is true, features such as timeouts should be disabled or
/// have minimum durations increased.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.accessibilityFeatures], where the setting originates.
final bool accessibleNavigation;
/// Whether the device is inverting the colors of the platform.
///
/// This flag is currently only updated on iOS devices.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.accessibilityFeatures], where the setting
/// originates.
final bool invertColors;
/// Whether the user requested a high contrast between foreground and background
/// content on iOS, via Settings -> Accessibility -> Increase Contrast.
///
/// This flag is currently only updated on iOS devices that are running iOS 13
/// or above.
final bool highContrast;
/// Whether the platform is requesting that animations be disabled or reduced
/// as much as possible.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.accessibilityFeatures], where the setting
/// originates.
final bool disableAnimations;
/// Whether the platform is requesting that text be drawn with a bold font
/// weight.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [dart:ui.PlatformDispatcher.accessibilityFeatures], where the setting
/// originates.
final bool boldText;
/// Describes the navigation mode requested by the platform.
///
/// Some user interfaces are better navigated using a directional pad (DPAD)
/// or arrow keys, and for those interfaces, some widgets need to handle these
/// directional events differently. In order to know when to do that, these
/// widgets will look for the navigation mode in effect for their context.
///
/// For instance, in a television interface, [NavigationMode.directional]
/// should be set, so that directional navigation is used to navigate away
/// from a text field using the DPAD. In contrast, on a regular desktop
/// application with the `navigationMode` set to [NavigationMode.traditional],
/// the arrow keys are used to move the cursor instead of navigating away.
///
/// The [NavigationMode] values indicate the type of navigation to be used in
/// a widget subtree for those widgets sensitive to it.
final NavigationMode navigationMode;
/// The orientation of the media (e.g., whether the device is in landscape or
/// portrait mode).
Orientation get orientation {
return size.width > size.height ? Orientation.landscape : Orientation.portrait;
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given fields replaced
/// with the new values.
MediaQueryData copyWith({
Size? size,
double? devicePixelRatio,
double? textScaleFactor,
Brightness? platformBrightness,
EdgeInsets? padding,
EdgeInsets? viewPadding,
EdgeInsets? viewInsets,
EdgeInsets? systemGestureInsets,
bool? alwaysUse24HourFormat,
bool? highContrast,
bool? disableAnimations,
bool? invertColors,
bool? accessibleNavigation,
bool? boldText,
NavigationMode? navigationMode,
}) {
return MediaQueryData(
size: size ?? this.size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio ?? this.devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor ?? this.textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness ?? this.platformBrightness,
padding: padding ?? this.padding,
viewPadding: viewPadding ?? this.viewPadding,
viewInsets: viewInsets ?? this.viewInsets,
systemGestureInsets: systemGestureInsets ?? this.systemGestureInsets,
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat ?? this.alwaysUse24HourFormat,
invertColors: invertColors ?? this.invertColors,
highContrast: highContrast ?? this.highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations ?? this.disableAnimations,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation ?? this.accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText ?? this.boldText,
navigationMode: navigationMode ?? this.navigationMode,
);
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given [padding]s
/// replaced with zero.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then this
/// [MediaQueryData] is returned unmodified.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.removePadding], which uses this method to remove [padding]
/// from the ambient [MediaQuery].
/// * [SafeArea], which both removes the padding from the [MediaQuery] and
/// adds a [Padding] widget.
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [viewInsets].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for [viewPadding].
MediaQueryData removePadding({
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
}) {
if (!(removeLeft || removeTop || removeRight || removeBottom))
return this;
return MediaQueryData(
size: size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness,
padding: padding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
viewPadding: viewPadding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.left - padding.left) : null,
top: removeTop ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.top - padding.top) : null,
right: removeRight ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.right - padding.right) : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.bottom - padding.bottom) : null,
),
viewInsets: viewInsets,
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast: highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations,
invertColors: invertColors,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText,
);
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given [viewInsets]
/// replaced with zero.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then this
/// [MediaQueryData] is returned unmodified.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.removeViewInsets], which uses this method to remove
/// [viewInsets] from the ambient [MediaQuery].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [padding].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for [viewPadding].
MediaQueryData removeViewInsets({
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
}) {
if (!(removeLeft || removeTop || removeRight || removeBottom))
return this;
return MediaQueryData(
size: size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness,
padding: padding,
viewPadding: viewPadding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.left - viewInsets.left) : null,
top: removeTop ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.top - viewInsets.top) : null,
right: removeRight ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.right - viewInsets.right) : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.bottom - viewInsets.bottom) : null,
),
viewInsets: viewInsets.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast: highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations,
invertColors: invertColors,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText,
);
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given [viewPadding]
/// replaced with zero.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then this
/// [MediaQueryData] is returned unmodified.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.removeViewPadding], which uses this method to remove
/// [viewPadding] from the ambient [MediaQuery].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [padding].
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [viewInsets].
MediaQueryData removeViewPadding({
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
}) {
if (!(removeLeft || removeTop || removeRight || removeBottom))
return this;
return MediaQueryData(
size: size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness,
padding: padding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
viewInsets: viewInsets,
viewPadding: viewPadding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast: highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations,
invertColors: invertColors,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText,
);
}
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) {
if (other.runtimeType != runtimeType)
return false;
return other is MediaQueryData
&& other.size == size
&& other.devicePixelRatio == devicePixelRatio
&& other.textScaleFactor == textScaleFactor
&& other.platformBrightness == platformBrightness
&& other.padding == padding
&& other.viewPadding == viewPadding
&& other.viewInsets == viewInsets
&& other.alwaysUse24HourFormat == alwaysUse24HourFormat
&& other.highContrast == highContrast
&& other.disableAnimations == disableAnimations
&& other.invertColors == invertColors
&& other.accessibleNavigation == accessibleNavigation
&& other.boldText == boldText
&& other.navigationMode == navigationMode;
}
@override
int get hashCode {
return hashValues(
size,
devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness,
padding,
viewPadding,
viewInsets,
alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast,
disableAnimations,
invertColors,
accessibleNavigation,
boldText,
navigationMode,
);
}
@override
String toString() {
final List<String> properties = <String>[
'size: $size',
'devicePixelRatio: ${devicePixelRatio.toStringAsFixed(1)}',
'textScaleFactor: ${textScaleFactor.toStringAsFixed(1)}',
'platformBrightness: $platformBrightness',
'padding: $padding',
'viewPadding: $viewPadding',
'viewInsets: $viewInsets',
'alwaysUse24HourFormat: $alwaysUse24HourFormat',
'accessibleNavigation: $accessibleNavigation',
'highContrast: $highContrast',
'disableAnimations: $disableAnimations',
'invertColors: $invertColors',
'boldText: $boldText',
'navigationMode: ${describeEnum(navigationMode)}',
];
return '${objectRuntimeType(this, 'MediaQueryData')}(${properties.join(', ')})';
}
}
/// Establishes a subtree in which media queries resolve to the given data.
///
/// For example, to learn the size of the current media (e.g., the window
/// containing your app), you can read the [MediaQueryData.size] property from
/// the [MediaQueryData] returned by [MediaQuery.of]:
/// `MediaQuery.of(context).size`.
///
/// Querying the current media using [MediaQuery.of] will cause your widget to
/// rebuild automatically whenever the [MediaQueryData] changes (e.g., if the
/// user rotates their device).
///
/// If no [MediaQuery] is in scope then the [MediaQuery.of] method will throw an
/// exception. Alternatively, [MediaQuery.maybeOf] may be used, which returns
/// null instead of throwing if no [MediaQuery] is in scope.
///
/// {@youtube 560 315 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A3WrA4zAaPw}
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [WidgetsApp] and [MaterialApp], which introduce a [MediaQuery] and keep
/// it up to date with the current screen metrics as they change.
/// * [MediaQueryData], the data structure that represents the metrics.
class MediaQuery extends InheritedWidget {
/// Creates a widget that provides [MediaQueryData] to its descendants.
///
/// The [data] and [child] arguments must not be null.
const MediaQuery({
Key? key,
required this.data,
required Widget child,
}) : assert(child != null),
assert(data != null),
super(key: key, child: child);
/// Creates a new [MediaQuery] that inherits from the ambient [MediaQuery]
/// from the given context, but removes the specified padding.
///
/// This should be inserted into the widget tree when the [MediaQuery] padding
/// is consumed by a widget in such a way that the padding is no longer
/// exposed to the widget's descendants or siblings.
///
/// The [context] argument is required, must not be null, and must have a
/// [MediaQuery] in scope.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then the returned
/// [MediaQuery] reuses the ambient [MediaQueryData] unmodified, which is not
/// particularly useful.
///
/// The [child] argument is required and must not be null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SafeArea], which both removes the padding from the [MediaQuery] and
/// adds a [Padding] widget.
/// * [MediaQueryData.padding], the affected property of the
/// [MediaQueryData].
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.viewInsets].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for
/// [MediaQueryData.viewPadding].
factory MediaQuery.removePadding({
Key? key,
required BuildContext context,
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
required Widget child,
}) {
return MediaQuery(
key: key,
data: MediaQuery.of(context).removePadding(
removeLeft: removeLeft,
removeTop: removeTop,
removeRight: removeRight,
removeBottom: removeBottom,
),
child: child,
);
}
/// Creates a new [MediaQuery] that inherits from the ambient [MediaQuery]
/// from the given context, but removes the specified view insets.
///
/// This should be inserted into the widget tree when the [MediaQuery] view
/// insets are consumed by a widget in such a way that the view insets are no
/// longer exposed to the widget's descendants or siblings.
///
/// The [context] argument is required, must not be null, and must have a
/// [MediaQuery] in scope.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then the returned
/// [MediaQuery] reuses the ambient [MediaQueryData] unmodified, which is not
/// particularly useful.
///
/// The [child] argument is required and must not be null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQueryData.viewInsets], the affected property of the
/// [MediaQueryData].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.padding].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for
/// [MediaQueryData.viewPadding].
factory MediaQuery.removeViewInsets({
Key? key,
required BuildContext context,
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
required Widget child,
}) {
return MediaQuery(
key: key,
data: MediaQuery.of(context).removeViewInsets(
removeLeft: removeLeft,
removeTop: removeTop,
removeRight: removeRight,
removeBottom: removeBottom,
),
child: child,
);
}
/// Creates a new [MediaQuery] that inherits from the ambient [MediaQuery]
/// from the given context, but removes the specified view padding.
///
/// This should be inserted into the widget tree when the [MediaQuery] view
/// padding is consumed by a widget in such a way that the view padding is no
/// longer exposed to the widget's descendants or siblings.
///
/// The [context] argument is required, must not be null, and must have a
/// [MediaQuery] in scope.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then the returned
/// [MediaQuery] reuses the ambient [MediaQueryData] unmodified, which is not
/// particularly useful.
///
/// The [child] argument is required and must not be null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQueryData.viewPadding], the affected property of the
/// [MediaQueryData].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.padding].
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.viewInsets].
factory MediaQuery.removeViewPadding({
Key? key,
required BuildContext context,
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
required Widget child,
}) {
return MediaQuery(
key: key,
data: MediaQuery.of(context).removeViewPadding(
removeLeft: removeLeft,
removeTop: removeTop,
removeRight: removeRight,
removeBottom: removeBottom,
),
child: child,
);
}
/// Contains information about the current media.
///
/// For example, the [MediaQueryData.size] property contains the width and
/// height of the current window.
final MediaQueryData data;
/// The data from the closest instance of this class that encloses the given
/// context.
///
/// You can use this function to query the size and orientation of the screen,
/// as well as other media parameters (see [MediaQueryData] for more
/// examples). When that information changes, your widget will be scheduled to
/// be rebuilt, keeping your widget up-to-date.
///
/// Typical usage is as follows:
///
/// ```dart
/// MediaQueryData media = MediaQuery.of(context);
/// ```
///
/// If there is no [MediaQuery] in scope, this will throw a [TypeError]
/// exception in release builds, and throw a descriptive [FlutterError] in
/// debug builds.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [maybeOf], which doesn't throw or assert if it doesn't find a
/// [MediaQuery] ancestor, it returns null instead.
static MediaQueryData of(BuildContext context) {
assert(context != null);
assert(debugCheckHasMediaQuery(context));
return context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<MediaQuery>()!.data;
}
/// The data from the closest instance of this class that encloses the given
/// context, if any.
///
/// Use this function if you want to allow situations where no [MediaQuery] is
/// in scope. Prefer using [MediaQuery.of] in situations where a media query
/// is always expected to exist.
///
/// If there is no [MediaQuery] in scope, then this function will return null.
///
/// You can use this function to query the size and orientation of the screen,
/// as well as other media parameters (see [MediaQueryData] for more
/// examples). When that information changes, your widget will be scheduled to
/// be rebuilt, keeping your widget up-to-date.
///
/// Typical usage is as follows:
///
/// ```dart
/// MediaQueryData? mediaQuery = MediaQuery.maybeOf(context);
/// if (mediaQuery == null) {
/// // Do something else instead.
/// }
/// ```
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [of], which will throw if it doesn't find a [MediaQuery] ancestor,
/// instead of returning null.
static MediaQueryData? maybeOf(BuildContext context) {
assert(context != null);
return context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<MediaQuery>()?.data;
}
/// Returns textScaleFactor for the nearest MediaQuery ancestor or 1.0, if
/// no such ancestor exists.
static double textScaleFactorOf(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.maybeOf(context)?.textScaleFactor ?? 1.0;
}
/// Returns platformBrightness for the nearest MediaQuery ancestor or
/// [Brightness.light], if no such ancestor exists.
///
/// Use of this method will cause the given [context] to rebuild any time that
/// any property of the ancestor [MediaQuery] changes.
static Brightness platformBrightnessOf(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.maybeOf(context)?.platformBrightness ?? Brightness.light;
}
/// Returns highContrast for the nearest MediaQuery ancestor or false, if no
/// such ancestor exists.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQueryData.highContrast], which indicates the platform's
/// desire to increase contrast.
static bool highContrastOf(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.maybeOf(context)?.highContrast ?? false;
}
/// Returns the boldText accessibility setting for the nearest MediaQuery
/// ancestor, or false if no such ancestor exists.
static bool boldTextOverride(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.maybeOf(context)?.boldText ?? false;
}
@override
bool updateShouldNotify(MediaQuery oldWidget) => data != oldWidget.data;
@override
void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
super.debugFillProperties(properties);
properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<MediaQueryData>('data', data, showName: false));
}
}
/// Describes the navigation mode to be set by a [MediaQuery] widget.
///
/// The different modes indicate the type of navigation to be used in a widget
/// subtree for those widgets sensitive to it.
///
/// Use `MediaQuery.of(context).navigationMode` to determine the navigation mode
/// in effect for the given context. Use a [MediaQuery] widget to set the
/// navigation mode for its descendant widgets.
enum NavigationMode {
/// This indicates a traditional keyboard-and-mouse navigation modality.
///
/// This navigation mode is where the arrow keys can be used for secondary
/// modification operations, like moving sliders or cursors, and disabled
/// controls will lose focus and not be traversable.
traditional,
/// This indicates a directional-based navigation mode.
///
/// This navigation mode indicates that arrow keys should be reserved for
/// navigation operations, and secondary modifications operations, like moving
/// sliders or cursors, will use alternative bindings or be disabled.
///
/// Some behaviors are also affected by this mode. For instance, disabled
/// controls will retain focus when disabled, and will be able to receive
/// focus (although they remain disabled) when traversed.
directional,
}