// Copyright 2014 The Flutter Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file.
import 'dart:math' as math;
import 'package:flutter/gestures.dart';
import 'package:flutter/rendering.dart';
import 'basic.dart';
import 'debug.dart';
import 'focus_manager.dart';
import 'focus_scope.dart';
import 'framework.dart';
import 'media_query.dart';
import 'notification_listener.dart';
import 'primary_scroll_controller.dart';
import 'scroll_configuration.dart';
import 'scroll_controller.dart';
import 'scroll_notification.dart';
import 'scroll_physics.dart';
import 'scrollable.dart';
import 'sliver.dart';
import 'sliver_prototype_extent_list.dart';
import 'viewport.dart';
// Examples can assume:
// late int itemCount;
/// A representation of how a [ScrollView] should dismiss the on-screen
/// keyboard.
enum ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior {
/// `manual` means there is no automatic dismissal of the on-screen keyboard.
/// It is up to the client to dismiss the keyboard.
manual,
/// `onDrag` means that the [ScrollView] will dismiss an on-screen keyboard
/// when a drag begins.
onDrag,
}
/// A widget that scrolls.
///
/// Scrollable widgets consist of three pieces:
///
/// 1. A [Scrollable] widget, which listens for various user gestures and
/// implements the interaction design for scrolling.
/// 2. A viewport widget, such as [Viewport] or [ShrinkWrappingViewport], which
/// implements the visual design for scrolling by displaying only a portion
/// of the widgets inside the scroll view.
/// 3. One or more slivers, which are widgets that can be composed to created
/// various scrolling effects, such as lists, grids, and expanding headers.
///
/// [ScrollView] helps orchestrate these pieces by creating the [Scrollable] and
/// the viewport and deferring to its subclass to create the slivers.
///
/// To control the initial scroll offset of the scroll view, provide a
/// [controller] with its [ScrollController.initialScrollOffset] property set.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ListView], which is a commonly used [ScrollView] that displays a
/// scrolling, linear list of child widgets.
/// * [PageView], which is a scrolling list of child widgets that are each the
/// size of the viewport.
/// * [GridView], which is a [ScrollView] that displays a scrolling, 2D array
/// of child widgets.
/// * [CustomScrollView], which is a [ScrollView] that creates custom scroll
/// effects using slivers.
/// * [ScrollNotification] and [NotificationListener], which can be used to watch
/// the scroll position without using a [ScrollController].
abstract class ScrollView extends StatelessWidget {
/// Creates a widget that scrolls.
///
/// If the [primary] argument is true, the [controller] must be null.
///
/// If the [shrinkWrap] argument is true, the [center] argument must be null.
///
/// The [scrollDirection], [reverse], and [shrinkWrap] arguments must not be null.
///
/// The [anchor] argument must be non-null and in the range 0.0 to 1.0.
const ScrollView({
Key? key,
this.scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
this.reverse = false,
this.controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
this.scrollBehavior,
this.shrinkWrap = false,
this.center,
this.anchor = 0.0,
this.cacheExtent,
this.semanticChildCount,
this.dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
this.keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
this.restorationId,
this.clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(scrollDirection != null),
assert(reverse != null),
assert(shrinkWrap != null),
assert(dragStartBehavior != null),
assert(clipBehavior != null),
assert(!(controller != null && primary == true),
'Primary ScrollViews obtain their ScrollController via inheritance from a PrimaryScrollController widget. '
'You cannot both set primary to true and pass an explicit controller.',
),
assert(!shrinkWrap || center == null),
assert(anchor != null),
assert(anchor >= 0.0 && anchor <= 1.0),
assert(semanticChildCount == null || semanticChildCount >= 0),
primary = primary ?? controller == null && identical(scrollDirection, Axis.vertical),
physics = physics ?? (primary == true || (primary == null && controller == null && identical(scrollDirection, Axis.vertical)) ? const AlwaysScrollableScrollPhysics() : null),
super(key: key);
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.scrollDirection}
/// The axis along which the scroll view scrolls.
///
/// Defaults to [Axis.vertical].
/// {@endtemplate}
final Axis scrollDirection;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.reverse}
/// Whether the scroll view scrolls in the reading direction.
///
/// For example, if the reading direction is left-to-right and
/// [scrollDirection] is [Axis.horizontal], then the scroll view scrolls from
/// left to right when [reverse] is false and from right to left when
/// [reverse] is true.
///
/// Similarly, if [scrollDirection] is [Axis.vertical], then the scroll view
/// scrolls from top to bottom when [reverse] is false and from bottom to top
/// when [reverse] is true.
///
/// Defaults to false.
/// {@endtemplate}
final bool reverse;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.controller}
/// An object that can be used to control the position to which this scroll
/// view is scrolled.
///
/// Must be null if [primary] is true.
///
/// A [ScrollController] serves several purposes. It can be used to control
/// the initial scroll position (see [ScrollController.initialScrollOffset]).
/// It can be used to control whether the scroll view should automatically
/// save and restore its scroll position in the [PageStorage] (see
/// [ScrollController.keepScrollOffset]). It can be used to read the current
/// scroll position (see [ScrollController.offset]), or change it (see
/// [ScrollController.animateTo]).
/// {@endtemplate}
final ScrollController? controller;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.primary}
/// Whether this is the primary scroll view associated with the parent
/// [PrimaryScrollController].
///
/// When this is true, the scroll view is scrollable even if it does not have
/// sufficient content to actually scroll. Otherwise, by default the user can
/// only scroll the view if it has sufficient content. See [physics].
///
/// Also when true, the scroll view is used for default [ScrollAction]s. If a
/// ScrollAction is not handled by an otherwise focused part of the application,
/// the ScrollAction will be evaluated using this scroll view, for example,
/// when executing [Shortcuts] key events like page up and down.
///
/// On iOS, this also identifies the scroll view that will scroll to top in
/// response to a tap in the status bar.
/// {@endtemplate}
///
/// Defaults to true when [scrollDirection] is [Axis.vertical] and
/// [controller] is null.
final bool primary;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.physics}
/// How the scroll view should respond to user input.
///
/// For example, determines how the scroll view continues to animate after the
/// user stops dragging the scroll view.
///
/// Defaults to matching platform conventions. Furthermore, if [primary] is
/// false, then the user cannot scroll if there is insufficient content to
/// scroll, while if [primary] is true, they can always attempt to scroll.
///
/// To force the scroll view to always be scrollable even if there is
/// insufficient content, as if [primary] was true but without necessarily
/// setting it to true, provide an [AlwaysScrollableScrollPhysics] physics
/// object, as in:
///
/// ```dart
/// physics: const AlwaysScrollableScrollPhysics(),
/// ```
///
/// To force the scroll view to use the default platform conventions and not
/// be scrollable if there is insufficient content, regardless of the value of
/// [primary], provide an explicit [ScrollPhysics] object, as in:
///
/// ```dart
/// physics: const ScrollPhysics(),
/// ```
///
/// The physics can be changed dynamically (by providing a new object in a
/// subsequent build), but new physics will only take effect if the _class_ of
/// the provided object changes. Merely constructing a new instance with a
/// different configuration is insufficient to cause the physics to be
/// reapplied. (This is because the final object used is generated
/// dynamically, which can be relatively expensive, and it would be
/// inefficient to speculatively create this object each frame to see if the
/// physics should be updated.)
/// {@endtemplate}
///
/// If an explicit [ScrollBehavior] is provided to [scrollBehavior], the
/// [ScrollPhysics] provided by that behavior will take precedence after
/// [physics].
final ScrollPhysics? physics;
/// {@macro flutter.widgets.shadow.scrollBehavior}
///
/// [ScrollBehavior]s also provide [ScrollPhysics]. If an explicit
/// [ScrollPhysics] is provided in [physics], it will take precedence,
/// followed by [scrollBehavior], and then the inherited ancestor
/// [ScrollBehavior].
final ScrollBehavior? scrollBehavior;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.shrinkWrap}
/// Whether the extent of the scroll view in the [scrollDirection] should be
/// determined by the contents being viewed.
///
/// If the scroll view does not shrink wrap, then the scroll view will expand
/// to the maximum allowed size in the [scrollDirection]. If the scroll view
/// has unbounded constraints in the [scrollDirection], then [shrinkWrap] must
/// be true.
///
/// Shrink wrapping the content of the scroll view is significantly more
/// expensive than expanding to the maximum allowed size because the content
/// can expand and contract during scrolling, which means the size of the
/// scroll view needs to be recomputed whenever the scroll position changes.
///
/// Defaults to false.
///
/// {@youtube 560 315 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LUqDNnv_dh0}
/// {@endtemplate}
final bool shrinkWrap;
/// The first child in the [GrowthDirection.forward] growth direction.
///
/// Children after [center] will be placed in the [AxisDirection] determined
/// by [scrollDirection] and [reverse] relative to the [center]. Children
/// before [center] will be placed in the opposite of the axis direction
/// relative to the [center]. This makes the [center] the inflection point of
/// the growth direction.
///
/// The [center] must be the key of one of the slivers built by [buildSlivers].
///
/// Of the built-in subclasses of [ScrollView], only [CustomScrollView]
/// supports [center]; for that class, the given key must be the key of one of
/// the slivers in the [CustomScrollView.slivers] list.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [anchor], which controls where the [center] as aligned in the viewport.
final Key? center;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.anchor}
/// The relative position of the zero scroll offset.
///
/// For example, if [anchor] is 0.5 and the [AxisDirection] determined by
/// [scrollDirection] and [reverse] is [AxisDirection.down] or
/// [AxisDirection.up], then the zero scroll offset is vertically centered
/// within the viewport. If the [anchor] is 1.0, and the axis direction is
/// [AxisDirection.right], then the zero scroll offset is on the left edge of
/// the viewport.
/// {@endtemplate}
final double anchor;
/// {@macro flutter.rendering.RenderViewportBase.cacheExtent}
final double? cacheExtent;
/// The number of children that will contribute semantic information.
///
/// Some subtypes of [ScrollView] can infer this value automatically. For
/// example [ListView] will use the number of widgets in the child list,
/// while the [ListView.separated] constructor will use half that amount.
///
/// For [CustomScrollView] and other types which do not receive a builder
/// or list of widgets, the child count must be explicitly provided. If the
/// number is unknown or unbounded this should be left unset or set to null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SemanticsConfiguration.scrollChildCount], the corresponding semantics property.
final int? semanticChildCount;
/// {@macro flutter.widgets.scrollable.dragStartBehavior}
final DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.scroll_view.keyboardDismissBehavior}
/// [ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior] the defines how this [ScrollView] will
/// dismiss the keyboard automatically.
/// {@endtemplate}
final ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior;
/// {@macro flutter.widgets.scrollable.restorationId}
final String? restorationId;
/// {@macro flutter.material.Material.clipBehavior}
///
/// Defaults to [Clip.hardEdge].
final Clip clipBehavior;
/// Returns the [AxisDirection] in which the scroll view scrolls.
///
/// Combines the [scrollDirection] with the [reverse] boolean to obtain the
/// concrete [AxisDirection].
///
/// If the [scrollDirection] is [Axis.horizontal], the ambient
/// [Directionality] is also considered when selecting the concrete
/// [AxisDirection]. For example, if the ambient [Directionality] is
/// [TextDirection.rtl], then the non-reversed [AxisDirection] is
/// [AxisDirection.left] and the reversed [AxisDirection] is
/// [AxisDirection.right].
@protected
AxisDirection getDirection(BuildContext context) {
return getAxisDirectionFromAxisReverseAndDirectionality(context, scrollDirection, reverse);
}
/// Build the list of widgets to place inside the viewport.
///
/// Subclasses should override this method to build the slivers for the inside
/// of the viewport.
@protected
List<Widget> buildSlivers(BuildContext context);
/// Build the viewport.
///
/// Subclasses may override this method to change how the viewport is built.
/// The default implementation uses a [ShrinkWrappingViewport] if [shrinkWrap]
/// is true, and a regular [Viewport] otherwise.
///
/// The `offset` argument is the value obtained from
/// [Scrollable.viewportBuilder].
///
/// The `axisDirection` argument is the value obtained from [getDirection],
/// which by default uses [scrollDirection] and [reverse].
///
/// The `slivers` argument is the value obtained from [buildSlivers].
@protected
Widget buildViewport(
BuildContext context,
ViewportOffset offset,
AxisDirection axisDirection,
List<Widget> slivers,
) {
assert(() {
switch (axisDirection) {
case AxisDirection.up:
case AxisDirection.down:
return debugCheckHasDirectionality(
context,
why: 'to determine the cross-axis direction of the scroll view',
hint: 'Vertical scroll views create Viewport widgets that try to determine their cross axis direction '
'from the ambient Directionality.',
);
case AxisDirection.left:
case AxisDirection.right:
return true;
}
}());
if (shrinkWrap) {
return ShrinkWrappingViewport(
axisDirection: axisDirection,
offset: offset,
slivers: slivers,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
}
return Viewport(
axisDirection: axisDirection,
offset: offset,
slivers: slivers,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
center: center,
anchor: anchor,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final List<Widget> slivers = buildSlivers(context);
final AxisDirection axisDirection = getDirection(context);
final ScrollController? scrollController =
primary ? PrimaryScrollController.of(context) : controller;
final Scrollable scrollable = Scrollable(
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
axisDirection: axisDirection,
controller: scrollController,
physics: physics,
scrollBehavior: scrollBehavior,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount,
restorationId: restorationId,
viewportBuilder: (BuildContext context, ViewportOffset offset) {
return buildViewport(context, offset, axisDirection, slivers);
},
);
final Widget scrollableResult = primary && scrollController != null
? PrimaryScrollController.none(child: scrollable)
: scrollable;
if (keyboardDismissBehavior == ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.onDrag) {
return NotificationListener<ScrollUpdateNotification>(
child: scrollableResult,
onNotification: (ScrollUpdateNotification notification) {
final FocusScopeNode focusScope = FocusScope.of(context);
if (notification.dragDetails != null && focusScope.hasFocus) {
focusScope.unfocus();
}
return false;
},
);
} else {
return scrollableResult;
}
}
@override
void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
super.debugFillProperties(properties);
properties.add(EnumProperty<Axis>('scrollDirection', scrollDirection));
properties.add(FlagProperty('reverse', value: reverse, ifTrue: 'reversed', showName: true));
properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<ScrollController>('controller', controller, showName: false, defaultValue: null));
properties.add(FlagProperty('primary', value: primary, ifTrue: 'using primary controller', showName: true));
properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<ScrollPhysics>('physics', physics, showName: false, defaultValue: null));
properties.add(FlagProperty('shrinkWrap', value: shrinkWrap, ifTrue: 'shrink-wrapping', showName: true));
}
}
/// A [ScrollView] that creates custom scroll effects using slivers.
///
/// A [CustomScrollView] lets you supply [slivers] directly to create various
/// scrolling effects, such as lists, grids, and expanding headers. For example,
/// to create a scroll view that contains an expanding app bar followed by a
/// list and a grid, use a list of three slivers: [SliverAppBar], [SliverList],
/// and [SliverGrid].
///
/// [Widget]s in these [slivers] must produce [RenderSliver] objects.
///
/// To control the initial scroll offset of the scroll view, provide a
/// [controller] with its [ScrollController.initialScrollOffset] property set.
///
/// {@animation 400 376 https://flutter.github.io/assets-for-api-docs/assets/widgets/custom_scroll_view.mp4}
///
/// {@tool snippet}
///
/// This sample code shows a scroll view that contains a flexible pinned app
/// bar, a grid, and an infinite list.
///
/// ```dart
/// CustomScrollView(
/// slivers: <Widget>[
/// const SliverAppBar(
/// pinned: true,
/// expandedHeight: 250.0,
/// flexibleSpace: FlexibleSpaceBar(
/// title: Text('Demo'),
/// ),
/// ),
/// SliverGrid(
/// gridDelegate: const SliverGridDelegateWithMaxCrossAxisExtent(
/// maxCrossAxisExtent: 200.0,
/// mainAxisSpacing: 10.0,
/// crossAxisSpacing: 10.0,
/// childAspectRatio: 4.0,
/// ),
/// delegate: SliverChildBuilderDelegate(
/// (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return Container(
/// alignment: Alignment.center,
/// color: Colors.teal[100 * (index % 9)],
/// child: Text('Grid Item $index'),
/// );
/// },
/// childCount: 20,
/// ),
/// ),
/// SliverFixedExtentList(
/// itemExtent: 50.0,
/// delegate: SliverChildBuilderDelegate(
/// (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return Container(
/// alignment: Alignment.center,
/// color: Colors.lightBlue[100 * (index % 9)],
/// child: Text('List Item $index'),
/// );
/// },
/// ),
/// ),
/// ],
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// {@tool dartpad}
/// By default, if items are inserted at the "top" of a scrolling container like
/// [ListView] or [CustomScrollView], the top item and all of the items below it
/// are scrolled downwards. In some applications, it's preferable to have the
/// top of the list just grow upwards, without changing the scroll position.
/// This example demonstrates how to do that with a [CustomScrollView] with
/// two [SliverList] children, and the [CustomScrollView.center] set to the key
/// of the bottom SliverList. The top one SliverList will grow upwards, and the
/// bottom SliverList will grow downwards.
///
/// ** See code in examples/api/lib/widgets/scroll_view/custom_scroll_view.1.dart **
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// ## Accessibility
///
/// A [CustomScrollView] can allow Talkback/VoiceOver to make announcements
/// to the user when the scroll state changes. For example, on Android an
/// announcement might be read as "showing items 1 to 10 of 23". To produce
/// this announcement, the scroll view needs three pieces of information:
///
/// * The first visible child index.
/// * The total number of children.
/// * The total number of visible children.
///
/// The last value can be computed exactly by the framework, however the first
/// two must be provided. Most of the higher-level scrollable widgets provide
/// this information automatically. For example, [ListView] provides each child
/// widget with a semantic index automatically and sets the semantic child
/// count to the length of the list.
///
/// To determine visible indexes, the scroll view needs a way to associate the
/// generated semantics of each scrollable item with a semantic index. This can
/// be done by wrapping the child widgets in an [IndexedSemantics].
///
/// This semantic index is not necessarily the same as the index of the widget in
/// the scrollable, because some widgets may not contribute semantic
/// information. Consider a [ListView.separated]: every other widget is a
/// divider with no semantic information. In this case, only odd numbered
/// widgets have a semantic index (equal to the index ~/ 2). Furthermore, the
/// total number of children in this example would be half the number of
/// widgets. (The [ListView.separated] constructor handles this
/// automatically; this is only used here as an example.)
///
/// The total number of visible children can be provided by the constructor
/// parameter `semanticChildCount`. This should always be the same as the
/// number of widgets wrapped in [IndexedSemantics].
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SliverList], which is a sliver that displays linear list of children.
/// * [SliverFixedExtentList], which is a more efficient sliver that displays
/// linear list of children that have the same extent along the scroll axis.
/// * [SliverGrid], which is a sliver that displays a 2D array of children.
/// * [SliverPadding], which is a sliver that adds blank space around another
/// sliver.
/// * [SliverAppBar], which is a sliver that displays a header that can expand
/// and float as the scroll view scrolls.
/// * [ScrollNotification] and [NotificationListener], which can be used to watch
/// the scroll position without using a [ScrollController].
/// * [IndexedSemantics], which allows annotating child lists with an index
/// for scroll announcements.
class CustomScrollView extends ScrollView {
/// Creates a [ScrollView] that creates custom scroll effects using slivers.
///
/// See the [ScrollView] constructor for more details on these arguments.
const CustomScrollView({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
ScrollBehavior? scrollBehavior,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
Key? center,
double anchor = 0.0,
double? cacheExtent,
this.slivers = const <Widget>[],
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
scrollBehavior: scrollBehavior,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
center: center,
anchor: anchor,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// The slivers to place inside the viewport.
final List<Widget> slivers;
@override
List<Widget> buildSlivers(BuildContext context) => slivers;
}
/// A [ScrollView] that uses a single child layout model.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ListView], which is a [BoxScrollView] that uses a linear layout model.
/// * [GridView], which is a [BoxScrollView] that uses a 2D layout model.
/// * [CustomScrollView], which can combine multiple child layout models into a
/// single scroll view.
abstract class BoxScrollView extends ScrollView {
/// Creates a [ScrollView] uses a single child layout model.
///
/// If the [primary] argument is true, the [controller] must be null.
const BoxScrollView({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
this.padding,
double? cacheExtent,
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// The amount of space by which to inset the children.
final EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding;
@override
List<Widget> buildSlivers(BuildContext context) {
Widget sliver = buildChildLayout(context);
EdgeInsetsGeometry? effectivePadding = padding;
if (padding == null) {
final MediaQueryData? mediaQuery = MediaQuery.maybeOf(context);
if (mediaQuery != null) {
// Automatically pad sliver with padding from MediaQuery.
final EdgeInsets mediaQueryHorizontalPadding =
mediaQuery.padding.copyWith(top: 0.0, bottom: 0.0);
final EdgeInsets mediaQueryVerticalPadding =
mediaQuery.padding.copyWith(left: 0.0, right: 0.0);
// Consume the main axis padding with SliverPadding.
effectivePadding = scrollDirection == Axis.vertical
? mediaQueryVerticalPadding
: mediaQueryHorizontalPadding;
// Leave behind the cross axis padding.
sliver = MediaQuery(
data: mediaQuery.copyWith(
padding: scrollDirection == Axis.vertical
? mediaQueryHorizontalPadding
: mediaQueryVerticalPadding,
),
child: sliver,
);
}
}
if (effectivePadding != null)
sliver = SliverPadding(padding: effectivePadding, sliver: sliver);
return <Widget>[ sliver ];
}
/// Subclasses should override this method to build the layout model.
@protected
Widget buildChildLayout(BuildContext context);
@override
void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
super.debugFillProperties(properties);
properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<EdgeInsetsGeometry>('padding', padding, defaultValue: null));
}
}
/// A scrollable list of widgets arranged linearly.
///
/// {@youtube 560 315 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KJpkjHGiI5A}
///
/// [ListView] is the most commonly used scrolling widget. It displays its
/// children one after another in the scroll direction. In the cross axis, the
/// children are required to fill the [ListView].
///
/// If non-null, the [itemExtent] forces the children to have the given extent
/// in the scroll direction.
///
/// If non-null, the [prototypeItem] forces the children to have the same extent
/// as the given widget in the scroll direction.
///
/// Specifying an [itemExtent] or an [prototypeItem] is more efficient than
/// letting the children determine their own extent because the scrolling
/// machinery can make use of the foreknowledge of the children's extent to save
/// work, for example when the scroll position changes drastically.
///
/// You can't specify both [itemExtent] and [prototypeItem], only one or none of
/// them.
///
/// There are four options for constructing a [ListView]:
///
/// 1. The default constructor takes an explicit [List<Widget>] of children. This
/// constructor is appropriate for list views with a small number of
/// children because constructing the [List] requires doing work for every
/// child that could possibly be displayed in the list view instead of just
/// those children that are actually visible.
///
/// 2. The [ListView.builder] constructor takes an [IndexedWidgetBuilder], which
/// builds the children on demand. This constructor is appropriate for list views
/// with a large (or infinite) number of children because the builder is called
/// only for those children that are actually visible.
///
/// 3. The [ListView.separated] constructor takes two [IndexedWidgetBuilder]s:
/// `itemBuilder` builds child items on demand, and `separatorBuilder`
/// similarly builds separator children which appear in between the child items.
/// This constructor is appropriate for list views with a fixed number of children.
///
/// 4. The [ListView.custom] constructor takes a [SliverChildDelegate], which provides
/// the ability to customize additional aspects of the child model. For example,
/// a [SliverChildDelegate] can control the algorithm used to estimate the
/// size of children that are not actually visible.
///
/// To control the initial scroll offset of the scroll view, provide a
/// [controller] with its [ScrollController.initialScrollOffset] property set.
///
/// By default, [ListView] will automatically pad the list's scrollable
/// extremities to avoid partial obstructions indicated by [MediaQuery]'s
/// padding. To avoid this behavior, override with a zero [padding] property.
///
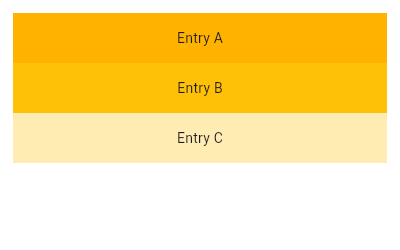
/// {@tool snippet}
/// This example uses the default constructor for [ListView] which takes an
/// explicit [List<Widget>] of children. This [ListView]'s children are made up
/// of [Container]s with [Text].
///
/// 
///
/// ```dart
/// ListView(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// children: <Widget>[
/// Container(
/// height: 50,
/// color: Colors.amber[600],
/// child: const Center(child: Text('Entry A')),
/// ),
/// Container(
/// height: 50,
/// color: Colors.amber[500],
/// child: const Center(child: Text('Entry B')),
/// ),
/// Container(
/// height: 50,
/// color: Colors.amber[100],
/// child: const Center(child: Text('Entry C')),
/// ),
/// ],
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
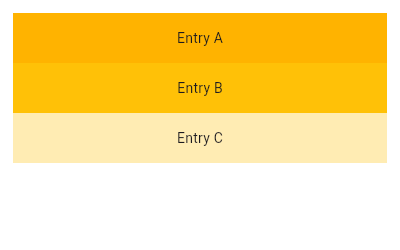
/// {@tool snippet}
/// This example mirrors the previous one, creating the same list using the
/// [ListView.builder] constructor. Using the [IndexedWidgetBuilder], children
/// are built lazily and can be infinite in number.
///
/// 
///
/// ```dart
/// final List<String> entries = <String>['A', 'B', 'C'];
/// final List<int> colorCodes = <int>[600, 500, 100];
///
/// ListView.builder(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// itemCount: entries.length,
/// itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return Container(
/// height: 50,
/// color: Colors.amber[colorCodes[index]],
/// child: Center(child: Text('Entry ${entries[index]}')),
/// );
/// }
/// );
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
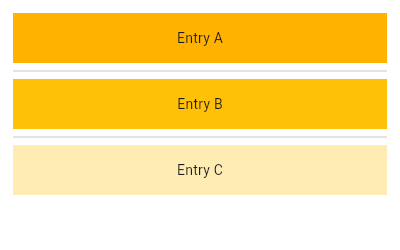
/// {@tool snippet}
/// This example continues to build from our the previous ones, creating a
/// similar list using [ListView.separated]. Here, a [Divider] is used as a
/// separator.
///
/// 
///
/// ```dart
/// final List<String> entries = <String>['A', 'B', 'C'];
/// final List<int> colorCodes = <int>[600, 500, 100];
///
/// ListView.separated(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// itemCount: entries.length,
/// itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return Container(
/// height: 50,
/// color: Colors.amber[colorCodes[index]],
/// child: Center(child: Text('Entry ${entries[index]}')),
/// );
/// },
/// separatorBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) => const Divider(),
/// );
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// ## Child elements' lifecycle
///
/// ### Creation
///
/// While laying out the list, visible children's elements, states and render
/// objects will be created lazily based on existing widgets (such as when using
/// the default constructor) or lazily provided ones (such as when using the
/// [ListView.builder] constructor).
///
/// ### Destruction
///
/// When a child is scrolled out of view, the associated element subtree,
/// states and render objects are destroyed. A new child at the same position
/// in the list will be lazily recreated along with new elements, states and
/// render objects when it is scrolled back.
///
/// ### Destruction mitigation
///
/// In order to preserve state as child elements are scrolled in and out of
/// view, the following options are possible:
///
/// * Moving the ownership of non-trivial UI-state-driving business logic
/// out of the list child subtree. For instance, if a list contains posts
/// with their number of upvotes coming from a cached network response, store
/// the list of posts and upvote number in a data model outside the list. Let
/// the list child UI subtree be easily recreate-able from the
/// source-of-truth model object. Use [StatefulWidget]s in the child
/// widget subtree to store instantaneous UI state only.
///
/// * Letting [KeepAlive] be the root widget of the list child widget subtree
/// that needs to be preserved. The [KeepAlive] widget marks the child
/// subtree's top render object child for keepalive. When the associated top
/// render object is scrolled out of view, the list keeps the child's render
/// object (and by extension, its associated elements and states) in a cache
/// list instead of destroying them. When scrolled back into view, the render
/// object is repainted as-is (if it wasn't marked dirty in the interim).
///
/// This only works if `addAutomaticKeepAlives` and `addRepaintBoundaries`
/// are false since those parameters cause the [ListView] to wrap each child
/// widget subtree with other widgets.
///
/// * Using [AutomaticKeepAlive] widgets (inserted by default when
/// `addAutomaticKeepAlives` is true). [AutomaticKeepAlive] allows descendant
/// widgets to control whether the subtree is actually kept alive or not.
/// This behavior is in contrast with [KeepAlive], which will unconditionally keep
/// the subtree alive.
///
/// As an example, the [EditableText] widget signals its list child element
/// subtree to stay alive while its text field has input focus. If it doesn't
/// have focus and no other descendants signaled for keepalive via a
/// [KeepAliveNotification], the list child element subtree will be destroyed
/// when scrolled away.
///
/// [AutomaticKeepAlive] descendants typically signal it to be kept alive
/// by using the [AutomaticKeepAliveClientMixin], then implementing the
/// [AutomaticKeepAliveClientMixin.wantKeepAlive] getter and calling
/// [AutomaticKeepAliveClientMixin.updateKeepAlive].
///
/// ## Transitioning to [CustomScrollView]
///
/// A [ListView] is basically a [CustomScrollView] with a single [SliverList] in
/// its [CustomScrollView.slivers] property.
///
/// If [ListView] is no longer sufficient, for example because the scroll view
/// is to have both a list and a grid, or because the list is to be combined
/// with a [SliverAppBar], etc, it is straight-forward to port code from using
/// [ListView] to using [CustomScrollView] directly.
///
/// The [key], [scrollDirection], [reverse], [controller], [primary], [physics],
/// and [shrinkWrap] properties on [ListView] map directly to the identically
/// named properties on [CustomScrollView].
///
/// The [CustomScrollView.slivers] property should be a list containing either:
/// * a [SliverList] if both [itemExtent] and [prototypeItem] were null;
/// * a [SliverFixedExtentList] if [itemExtent] was not null; or
/// * a [SliverPrototypeExtentList] if [prototypeItem] was not null.
///
/// The [childrenDelegate] property on [ListView] corresponds to the
/// [SliverList.delegate] (or [SliverFixedExtentList.delegate]) property. The
/// [ListView] constructor's `children` argument corresponds to the
/// [childrenDelegate] being a [SliverChildListDelegate] with that same
/// argument. The [ListView.builder] constructor's `itemBuilder` and
/// `itemCount` arguments correspond to the [childrenDelegate] being a
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate] with the equivalent arguments.
///
/// The [padding] property corresponds to having a [SliverPadding] in the
/// [CustomScrollView.slivers] property instead of the list itself, and having
/// the [SliverList] instead be a child of the [SliverPadding].
///
/// [CustomScrollView]s don't automatically avoid obstructions from [MediaQuery]
/// like [ListView]s do. To reproduce the behavior, wrap the slivers in
/// [SliverSafeArea]s.
///
/// Once code has been ported to use [CustomScrollView], other slivers, such as
/// [SliverGrid] or [SliverAppBar], can be put in the [CustomScrollView.slivers]
/// list.
///
/// {@tool snippet}
///
/// Here are two brief snippets showing a [ListView] and its equivalent using
/// [CustomScrollView]:
///
/// ```dart
/// ListView(
/// shrinkWrap: true,
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
/// children: const <Widget>[
/// Text("I'm dedicating every day to you"),
/// Text('Domestic life was never quite my style'),
/// Text('When you smile, you knock me out, I fall apart'),
/// Text('And I thought I was so smart'),
/// ],
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
/// {@tool snippet}
///
/// ```dart
/// CustomScrollView(
/// shrinkWrap: true,
/// slivers: <Widget>[
/// SliverPadding(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20.0),
/// sliver: SliverList(
/// delegate: SliverChildListDelegate(
/// <Widget>[
/// const Text("I'm dedicating every day to you"),
/// const Text('Domestic life was never quite my style'),
/// const Text('When you smile, you knock me out, I fall apart'),
/// const Text('And I thought I was so smart'),
/// ],
/// ),
/// ),
/// ),
/// ],
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// ## Special handling for an empty list
///
/// A common design pattern is to have a custom UI for an empty list. The best
/// way to achieve this in Flutter is just conditionally replacing the
/// [ListView] at build time with whatever widgets you need to show for the
/// empty list state:
///
/// {@tool snippet}
///
/// Example of simple empty list interface:
///
/// ```dart
/// Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// return Scaffold(
/// appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Empty List Test')),
/// body: itemCount > 0
/// ? ListView.builder(
/// itemCount: itemCount,
/// itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return ListTile(
/// title: Text('Item ${index + 1}'),
/// );
/// },
/// )
/// : const Center(child: Text('No items')),
/// );
/// }
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// ## Selection of list items
///
/// `ListView` has no built-in notion of a selected item or items. For a small
/// example of how a caller might wire up basic item selection, see
/// [ListTile.selected].
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SingleChildScrollView], which is a scrollable widget that has a single
/// child.
/// * [PageView], which is a scrolling list of child widgets that are each the
/// size of the viewport.
/// * [GridView], which is a scrollable, 2D array of widgets.
/// * [CustomScrollView], which is a scrollable widget that creates custom
/// scroll effects using slivers.
/// * [ListBody], which arranges its children in a similar manner, but without
/// scrolling.
/// * [ScrollNotification] and [NotificationListener], which can be used to watch
/// the scroll position without using a [ScrollController].
/// * The [catalog of layout widgets](https://flutter.dev/widgets/layout/).
/// * Cookbook: [Use lists](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/lists/basic-list)
/// * Cookbook: [Work with long lists](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/lists/long-lists)
/// * Cookbook: [Create a horizontal list](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/lists/horizontal-list)
/// * Cookbook: [Create lists with different types of items](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/lists/mixed-list)
/// * Cookbook: [Implement swipe to dismiss](https://flutter.dev/docs/cookbook/gestures/dismissible)
class ListView extends BoxScrollView {
/// Creates a scrollable, linear array of widgets from an explicit [List].
///
/// This constructor is appropriate for list views with a small number of
/// children because constructing the [List] requires doing work for every
/// child that could possibly be displayed in the list view instead of just
/// those children that are actually visible.
///
/// Like other widgets in the framework, this widget expects that
/// the [children] list will not be mutated after it has been passed in here.
/// See the documentation at [SliverChildListDelegate.children] for more details.
///
/// It is usually more efficient to create children on demand using
/// [ListView.builder] because it will create the widget children lazily as necessary.
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. The
/// `addSemanticIndexes` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addSemanticIndexes] property. None
/// may be null.
ListView({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
this.itemExtent,
this.prototypeItem,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(
itemExtent == null || prototypeItem == null,
'You can only pass itemExtent or prototypeItem, not both.',
),
childrenDelegate = SliverChildListDelegate(
children,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount ?? children.length,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a scrollable, linear array of widgets that are created on demand.
///
/// This constructor is appropriate for list views with a large (or infinite)
/// number of children because the builder is called only for those children
/// that are actually visible.
///
/// Providing a non-null `itemCount` improves the ability of the [ListView] to
/// estimate the maximum scroll extent.
///
/// The `itemBuilder` callback will be called only with indices greater than
/// or equal to zero and less than `itemCount`.
///
/// The `itemBuilder` should always return a non-null widget, and actually
/// create the widget instances when called. Avoid using a builder that
/// returns a previously-constructed widget; if the list view's children are
/// created in advance, or all at once when the [ListView] itself is created,
/// it is more efficient to use the [ListView] constructor. Even more
/// efficient, however, is to create the instances on demand using this
/// constructor's `itemBuilder` callback.
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. The
/// `addSemanticIndexes` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addSemanticIndexes] property. None may be
/// null.
///
/// [ListView.builder] by default does not support child reordering. If
/// you are planning to change child order at a later time, consider using
/// [ListView] or [ListView.custom].
ListView.builder({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
this.itemExtent,
this.prototypeItem,
required IndexedWidgetBuilder itemBuilder,
int? itemCount,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(itemCount == null || itemCount >= 0),
assert(semanticChildCount == null || semanticChildCount <= itemCount!),
assert(
itemExtent == null || prototypeItem == null,
'You can only pass itemExtent or prototypeItem, not both.',
),
childrenDelegate = SliverChildBuilderDelegate(
itemBuilder,
childCount: itemCount,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount ?? itemCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a fixed-length scrollable linear array of list "items" separated
/// by list item "separators".
///
/// This constructor is appropriate for list views with a large number of
/// item and separator children because the builders are only called for
/// the children that are actually visible.
///
/// The `itemBuilder` callback will be called with indices greater than
/// or equal to zero and less than `itemCount`.
///
/// Separators only appear between list items: separator 0 appears after item
/// 0 and the last separator appears before the last item.
///
/// The `separatorBuilder` callback will be called with indices greater than
/// or equal to zero and less than `itemCount - 1`.
///
/// The `itemBuilder` and `separatorBuilder` callbacks should always return a
/// non-null widget, and actually create widget instances when called. Avoid
/// using a builder that returns a previously-constructed widget; if the list
/// view's children are created in advance, or all at once when the [ListView]
/// itself is created, it is more efficient to use the [ListView] constructor.
///
/// {@tool snippet}
///
/// This example shows how to create [ListView] whose [ListTile] list items
/// are separated by [Divider]s.
///
/// ```dart
/// ListView.separated(
/// itemCount: 25,
/// separatorBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) => const Divider(),
/// itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return ListTile(
/// title: Text('item $index'),
/// );
/// },
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. The
/// `addSemanticIndexes` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addSemanticIndexes] property. None may be
/// null.
ListView.separated({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
required IndexedWidgetBuilder itemBuilder,
required IndexedWidgetBuilder separatorBuilder,
required int itemCount,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(itemBuilder != null),
assert(separatorBuilder != null),
assert(itemCount != null && itemCount >= 0),
itemExtent = null,
prototypeItem = null,
childrenDelegate = SliverChildBuilderDelegate(
(BuildContext context, int index) {
final int itemIndex = index ~/ 2;
final Widget widget;
if (index.isEven) {
widget = itemBuilder(context, itemIndex);
} else {
widget = separatorBuilder(context, itemIndex);
assert(() {
if (widget == null) {
throw FlutterError('separatorBuilder cannot return null.');
}
return true;
}());
}
return widget;
},
childCount: _computeActualChildCount(itemCount),
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
semanticIndexCallback: (Widget _, int index) {
return index.isEven ? index ~/ 2 : null;
},
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: itemCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a scrollable, linear array of widgets with a custom child model.
///
/// For example, a custom child model can control the algorithm used to
/// estimate the size of children that are not actually visible.
///
/// {@tool snippet}
///
/// This [ListView] uses a custom [SliverChildBuilderDelegate] to support child
/// reordering.
///
/// ```dart
/// class MyListView extends StatefulWidget {
/// const MyListView({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
///
/// @override
/// State<MyListView> createState() => _MyListViewState();
/// }
///
/// class _MyListViewState extends State<MyListView> {
/// List<String> items = <String>['1', '2', '3', '4', '5'];
///
/// void _reverse() {
/// setState(() {
/// items = items.reversed.toList();
/// });
/// }
///
/// @override
/// Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// return Scaffold(
/// body: SafeArea(
/// child: ListView.custom(
/// childrenDelegate: SliverChildBuilderDelegate(
/// (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return KeepAlive(
/// data: items[index],
/// key: ValueKey<String>(items[index]),
/// );
/// },
/// childCount: items.length,
/// findChildIndexCallback: (Key key) {
/// final ValueKey<String> valueKey = key as ValueKey<String>;
/// final String data = valueKey.value;
/// return items.indexOf(data);
/// }
/// ),
/// ),
/// ),
/// bottomNavigationBar: BottomAppBar(
/// child: Row(
/// mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
/// children: <Widget>[
/// TextButton(
/// onPressed: () => _reverse(),
/// child: const Text('Reverse items'),
/// ),
/// ],
/// ),
/// ),
/// );
/// }
/// }
///
/// class KeepAlive extends StatefulWidget {
/// const KeepAlive({
/// required Key key,
/// required this.data,
/// }) : super(key: key);
///
/// final String data;
///
/// @override
/// State<KeepAlive> createState() => _KeepAliveState();
/// }
///
/// class _KeepAliveState extends State<KeepAlive> with AutomaticKeepAliveClientMixin{
/// @override
/// bool get wantKeepAlive => true;
///
/// @override
/// Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// super.build(context);
/// return Text(widget.data);
/// }
/// }
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
const ListView.custom({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
this.itemExtent,
this.prototypeItem,
required this.childrenDelegate,
double? cacheExtent,
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(childrenDelegate != null),
assert(
itemExtent == null || prototypeItem == null,
'You can only pass itemExtent or prototypeItem, not both',
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// {@template flutter.widgets.list_view.itemExtent}
/// If non-null, forces the children to have the given extent in the scroll
/// direction.
///
/// Specifying an [itemExtent] is more efficient than letting the children
/// determine their own extent because the scrolling machinery can make use of
/// the foreknowledge of the children's extent to save work, for example when
/// the scroll position changes drastically.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SliverFixedExtentList], the sliver used internally when this property
/// is provided. It constrains its box children to have a specific given
/// extent along the main axis.
/// * The [prototypeItem] property, which allows forcing the children's
/// extent to be the same as the given widget.
/// {@endtemplate}
final double? itemExtent;
/// {@template flutter.widgets.list_view.prototypeItem}
/// If non-null, forces the children to have the same extent as the given
/// widget in the scroll direction.
///
/// Specifying an [prototypeItem] is more efficient than letting the children
/// determine their own extent because the scrolling machinery can make use of
/// the foreknowledge of the children's extent to save work, for example when
/// the scroll position changes drastically.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SliverPrototypeExtentList], the sliver used internally when this
/// property is provided. It constrains its box children to have the same
/// extent as a prototype item along the main axis.
/// * The [itemExtent] property, which allows forcing the children's extent
/// to a given value.
/// {@endtemplate}
final Widget? prototypeItem;
/// A delegate that provides the children for the [ListView].
///
/// The [ListView.custom] constructor lets you specify this delegate
/// explicitly. The [ListView] and [ListView.builder] constructors create a
/// [childrenDelegate] that wraps the given [List] and [IndexedWidgetBuilder],
/// respectively.
final SliverChildDelegate childrenDelegate;
@override
Widget buildChildLayout(BuildContext context) {
if (itemExtent != null) {
return SliverFixedExtentList(
delegate: childrenDelegate,
itemExtent: itemExtent!,
);
} else if (prototypeItem != null) {
return SliverPrototypeExtentList(
delegate: childrenDelegate,
prototypeItem: prototypeItem!,
);
}
return SliverList(delegate: childrenDelegate);
}
@override
void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
super.debugFillProperties(properties);
properties.add(DoubleProperty('itemExtent', itemExtent, defaultValue: null));
}
// Helper method to compute the actual child count for the separated constructor.
static int _computeActualChildCount(int itemCount) {
return math.max(0, itemCount * 2 - 1);
}
}
/// A scrollable, 2D array of widgets.
///
/// {@youtube 560 315 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bLOtZDTm4H8}
///
/// The main axis direction of a grid is the direction in which it scrolls (the
/// [scrollDirection]).
///
/// The most commonly used grid layouts are [GridView.count], which creates a
/// layout with a fixed number of tiles in the cross axis, and
/// [GridView.extent], which creates a layout with tiles that have a maximum
/// cross-axis extent. A custom [SliverGridDelegate] can produce an arbitrary 2D
/// arrangement of children, including arrangements that are unaligned or
/// overlapping.
///
/// To create a grid with a large (or infinite) number of children, use the
/// [GridView.builder] constructor with either a
/// [SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount] or a
/// [SliverGridDelegateWithMaxCrossAxisExtent] for the [gridDelegate].
///
/// To use a custom [SliverChildDelegate], use [GridView.custom].
///
/// To create a linear array of children, use a [ListView].
///
/// To control the initial scroll offset of the scroll view, provide a
/// [controller] with its [ScrollController.initialScrollOffset] property set.
///
/// ## Transitioning to [CustomScrollView]
///
/// A [GridView] is basically a [CustomScrollView] with a single [SliverGrid] in
/// its [CustomScrollView.slivers] property.
///
/// If [GridView] is no longer sufficient, for example because the scroll view
/// is to have both a grid and a list, or because the grid is to be combined
/// with a [SliverAppBar], etc, it is straight-forward to port code from using
/// [GridView] to using [CustomScrollView] directly.
///
/// The [key], [scrollDirection], [reverse], [controller], [primary], [physics],
/// and [shrinkWrap] properties on [GridView] map directly to the identically
/// named properties on [CustomScrollView].
///
/// The [CustomScrollView.slivers] property should be a list containing just a
/// [SliverGrid].
///
/// The [childrenDelegate] property on [GridView] corresponds to the
/// [SliverGrid.delegate] property, and the [gridDelegate] property on the
/// [GridView] corresponds to the [SliverGrid.gridDelegate] property.
///
/// The [GridView], [GridView.count], and [GridView.extent]
/// constructors' `children` arguments correspond to the [childrenDelegate]
/// being a [SliverChildListDelegate] with that same argument. The
/// [GridView.builder] constructor's `itemBuilder` and `childCount` arguments
/// correspond to the [childrenDelegate] being a [SliverChildBuilderDelegate]
/// with the matching arguments.
///
/// The [GridView.count] and [GridView.extent] constructors create
/// custom grid delegates, and have equivalently named constructors on
/// [SliverGrid] to ease the transition: [SliverGrid.count] and
/// [SliverGrid.extent] respectively.
///
/// The [padding] property corresponds to having a [SliverPadding] in the
/// [CustomScrollView.slivers] property instead of the grid itself, and having
/// the [SliverGrid] instead be a child of the [SliverPadding].
///
/// Once code has been ported to use [CustomScrollView], other slivers, such as
/// [SliverList] or [SliverAppBar], can be put in the [CustomScrollView.slivers]
/// list.
///
/// {@tool snippet}
/// This example demonstrates how to create a [GridView] with two columns. The
/// children are spaced apart using the `crossAxisSpacing` and `mainAxisSpacing`
/// properties.
///
/// 
///
/// ```dart
/// GridView.count(
/// primary: false,
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
/// crossAxisSpacing: 10,
/// mainAxisSpacing: 10,
/// crossAxisCount: 2,
/// children: <Widget>[
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text("He'd have you all unravel at the"),
/// color: Colors.teal[100],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Heed not the rabble'),
/// color: Colors.teal[200],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Sound of screams but the'),
/// color: Colors.teal[300],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Who scream'),
/// color: Colors.teal[400],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Revolution is coming...'),
/// color: Colors.teal[500],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Revolution, they...'),
/// color: Colors.teal[600],
/// ),
/// ],
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// {@tool snippet}
/// This example shows how to create the same grid as the previous example
/// using a [CustomScrollView] and a [SliverGrid].
///
/// 
///
/// ```dart
/// CustomScrollView(
/// primary: false,
/// slivers: <Widget>[
/// SliverPadding(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(20),
/// sliver: SliverGrid.count(
/// crossAxisSpacing: 10,
/// mainAxisSpacing: 10,
/// crossAxisCount: 2,
/// children: <Widget>[
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text("He'd have you all unravel at the"),
/// color: Colors.green[100],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Heed not the rabble'),
/// color: Colors.green[200],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Sound of screams but the'),
/// color: Colors.green[300],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Who scream'),
/// color: Colors.green[400],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Revolution is coming...'),
/// color: Colors.green[500],
/// ),
/// Container(
/// padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
/// child: const Text('Revolution, they...'),
/// color: Colors.green[600],
/// ),
/// ],
/// ),
/// ),
/// ],
/// )
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// By default, [GridView] will automatically pad the limits of the
/// grids's scrollable to avoid partial obstructions indicated by
/// [MediaQuery]'s padding. To avoid this behavior, override with a
/// zero [padding] property.
///
/// {@tool snippet}
/// The following example demonstrates how to override the default top padding
/// using [MediaQuery.removePadding].
///
/// ```dart
/// Widget myWidget(BuildContext context) {
/// return MediaQuery.removePadding(
/// context: context,
/// removeTop: true,
/// child: GridView.builder(
/// gridDelegate: const SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount(
/// crossAxisCount: 3,
/// ),
/// itemCount: 300,
/// itemBuilder: (BuildContext context, int index) {
/// return Card(
/// color: Colors.amber,
/// child: Center(child: Text('$index')),
/// );
/// }
/// ),
/// );
/// }
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SingleChildScrollView], which is a scrollable widget that has a single
/// child.
/// * [ListView], which is scrollable, linear list of widgets.
/// * [PageView], which is a scrolling list of child widgets that are each the
/// size of the viewport.
/// * [CustomScrollView], which is a scrollable widget that creates custom
/// scroll effects using slivers.
/// * [SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount], which creates a layout with
/// a fixed number of tiles in the cross axis.
/// * [SliverGridDelegateWithMaxCrossAxisExtent], which creates a layout with
/// tiles that have a maximum cross-axis extent.
/// * [ScrollNotification] and [NotificationListener], which can be used to watch
/// the scroll position without using a [ScrollController].
/// * The [catalog of layout widgets](https://flutter.dev/widgets/layout/).
class GridView extends BoxScrollView {
/// Creates a scrollable, 2D array of widgets with a custom
/// [SliverGridDelegate].
///
/// The [gridDelegate] argument must not be null.
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. Both must not be
/// null.
GridView({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
required this.gridDelegate,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
}) : assert(gridDelegate != null),
childrenDelegate = SliverChildListDelegate(
children,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount ?? children.length,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a scrollable, 2D array of widgets that are created on demand.
///
/// This constructor is appropriate for grid views with a large (or infinite)
/// number of children because the builder is called only for those children
/// that are actually visible.
///
/// Providing a non-null `itemCount` improves the ability of the [GridView] to
/// estimate the maximum scroll extent.
///
/// `itemBuilder` will be called only with indices greater than or equal to
/// zero and less than `itemCount`.
///
/// The [gridDelegate] argument must not be null.
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildBuilderDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. Both must not
/// be null.
GridView.builder({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
required this.gridDelegate,
required IndexedWidgetBuilder itemBuilder,
int? itemCount,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(gridDelegate != null),
childrenDelegate = SliverChildBuilderDelegate(
itemBuilder,
childCount: itemCount,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount ?? itemCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a scrollable, 2D array of widgets with both a custom
/// [SliverGridDelegate] and a custom [SliverChildDelegate].
///
/// To use an [IndexedWidgetBuilder] callback to build children, either use
/// a [SliverChildBuilderDelegate] or use the [GridView.builder] constructor.
///
/// The [gridDelegate] and [childrenDelegate] arguments must not be null.
const GridView.custom({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
required this.gridDelegate,
required this.childrenDelegate,
double? cacheExtent,
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : assert(gridDelegate != null),
assert(childrenDelegate != null),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a scrollable, 2D array of widgets with a fixed number of tiles in
/// the cross axis.
///
/// Uses a [SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount] as the [gridDelegate].
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. Both must not be
/// null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SliverGrid.count], the equivalent constructor for [SliverGrid].
GridView.count({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
required int crossAxisCount,
double mainAxisSpacing = 0.0,
double crossAxisSpacing = 0.0,
double childAspectRatio = 1.0,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : gridDelegate = SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount(
crossAxisCount: crossAxisCount,
mainAxisSpacing: mainAxisSpacing,
crossAxisSpacing: crossAxisSpacing,
childAspectRatio: childAspectRatio,
),
childrenDelegate = SliverChildListDelegate(
children,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount ?? children.length,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// Creates a scrollable, 2D array of widgets with tiles that each have a
/// maximum cross-axis extent.
///
/// Uses a [SliverGridDelegateWithMaxCrossAxisExtent] as the [gridDelegate].
///
/// The `addAutomaticKeepAlives` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addAutomaticKeepAlives] property. The
/// `addRepaintBoundaries` argument corresponds to the
/// [SliverChildListDelegate.addRepaintBoundaries] property. Both must not be
/// null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SliverGrid.extent], the equivalent constructor for [SliverGrid].
GridView.extent({
Key? key,
Axis scrollDirection = Axis.vertical,
bool reverse = false,
ScrollController? controller,
bool? primary,
ScrollPhysics? physics,
bool shrinkWrap = false,
EdgeInsetsGeometry? padding,
required double maxCrossAxisExtent,
double mainAxisSpacing = 0.0,
double crossAxisSpacing = 0.0,
double childAspectRatio = 1.0,
bool addAutomaticKeepAlives = true,
bool addRepaintBoundaries = true,
bool addSemanticIndexes = true,
double? cacheExtent,
List<Widget> children = const <Widget>[],
int? semanticChildCount,
DragStartBehavior dragStartBehavior = DragStartBehavior.start,
ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior keyboardDismissBehavior = ScrollViewKeyboardDismissBehavior.manual,
String? restorationId,
Clip clipBehavior = Clip.hardEdge,
}) : gridDelegate = SliverGridDelegateWithMaxCrossAxisExtent(
maxCrossAxisExtent: maxCrossAxisExtent,
mainAxisSpacing: mainAxisSpacing,
crossAxisSpacing: crossAxisSpacing,
childAspectRatio: childAspectRatio,
),
childrenDelegate = SliverChildListDelegate(
children,
addAutomaticKeepAlives: addAutomaticKeepAlives,
addRepaintBoundaries: addRepaintBoundaries,
addSemanticIndexes: addSemanticIndexes,
),
super(
key: key,
scrollDirection: scrollDirection,
reverse: reverse,
controller: controller,
primary: primary,
physics: physics,
shrinkWrap: shrinkWrap,
padding: padding,
cacheExtent: cacheExtent,
semanticChildCount: semanticChildCount ?? children.length,
dragStartBehavior: dragStartBehavior,
keyboardDismissBehavior: keyboardDismissBehavior,
restorationId: restorationId,
clipBehavior: clipBehavior,
);
/// A delegate that controls the layout of the children within the [GridView].
///
/// The [GridView], [GridView.builder], and [GridView.custom] constructors let you specify this
/// delegate explicitly. The other constructors create a [gridDelegate]
/// implicitly.
final SliverGridDelegate gridDelegate;
/// A delegate that provides the children for the [GridView].
///
/// The [GridView.custom] constructor lets you specify this delegate
/// explicitly. The other constructors create a [childrenDelegate] that wraps
/// the given child list.
final SliverChildDelegate childrenDelegate;
@override
Widget buildChildLayout(BuildContext context) {
return SliverGrid(
delegate: childrenDelegate,
gridDelegate: gridDelegate,
);
}
}