// Copyright 2014 The Flutter Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file.
import 'dart:math' as math;
import 'dart:ui' as ui;
import 'dart:ui' show Brightness;
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'basic.dart';
import 'framework.dart';
/// Whether in portrait or landscape.
enum Orientation {
/// Taller than wide.
portrait,
/// Wider than tall.
landscape
}
/// Information about a piece of media (e.g., a window).
///
/// For example, the [MediaQueryData.size] property contains the width and
/// height of the current window.
///
/// To obtain the current [MediaQueryData] for a given [BuildContext], use the
/// [MediaQuery.of] function. For example, to obtain the size of the current
/// window, use `MediaQuery.of(context).size`.
///
/// If no [MediaQuery] is in scope then the [MediaQuery.of] method will throw an
/// exception, unless the `nullOk` argument is set to true, in which case it
/// returns null.
///
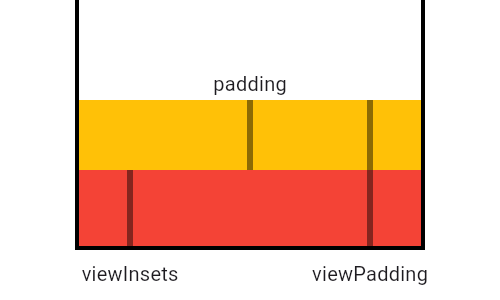
/// ## Insets and Padding
///
/// 
///
/// This diagram illustrates how [padding] relates to [viewPadding] and
/// [viewInsets], shown here in its simplest configuration, as the difference
/// between the two. In cases when the viewInsets exceed the viewPadding, like
/// when a software keyboard is shown below, padding goes to zero rather than a
/// negative value. Therefore, padding is calculated by taking
/// `max(0.0, viewPadding - viewInsets)`.
///
/// {@animation 300 300 https://flutter.github.io/assets-for-api-docs/assets/widgets/window_padding.mp4}
///
/// In this diagram, the black areas represent system UI that the app cannot
/// draw over. The red area represents view padding that the application may not
/// be able to detect gestures in and may not want to draw in. The grey area
/// represents the system keyboard, which can cover over the bottom view padding
/// when visible.
///
/// MediaQueryData includes three [EdgeInsets] values:
/// [padding], [viewPadding], and [viewInsets]. These values reflect the
/// configuration of the device and are used and optionally consumed by widgets
/// that position content within these insets. The padding value defines areas
/// that might not be completely visible, like the display "notch" on the iPhone
/// X. The viewInsets value defines areas that aren't visible at all, typically
/// because they're obscured by the device's keyboard. Similar to viewInsets,
/// viewPadding does not differentiate padding in areas that may be obscured.
/// For example, by using the viewPadding property, padding would defer to the
/// iPhone "safe area" regardless of whether a keyboard is showing.
///
/// The viewInsets and viewPadding are independent values, they're
/// measured from the edges of the MediaQuery widget's bounds. Together they
/// inform the [padding] property. The bounds of the top level MediaQuery
/// created by [WidgetsApp] are the same as the window that contains the app.
///
/// Widgets whose layouts consume space defined by [viewInsets], [viewPadding],
/// or [padding] should enclose their children in secondary MediaQuery
/// widgets that reduce those properties by the same amount.
/// The [removePadding], [removeViewPadding], and [removeViewInsets] methods are
/// useful for this.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [Scaffold], [SafeArea], [CupertinoTabScaffold], and
/// [CupertinoPageScaffold], all of which are informed by [padding],
/// [viewPadding], and [viewInsets].
@immutable
class MediaQueryData {
/// Creates data for a media query with explicit values.
///
/// Consider using [MediaQueryData.fromWindow] to create data based on a
/// [Window].
const MediaQueryData({
this.size = Size.zero,
this.devicePixelRatio = 1.0,
this.textScaleFactor = 1.0,
this.platformBrightness = Brightness.light,
this.padding = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.viewInsets = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.systemGestureInsets = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.viewPadding = EdgeInsets.zero,
this.physicalDepth = double.maxFinite,
this.alwaysUse24HourFormat = false,
this.accessibleNavigation = false,
this.invertColors = false,
this.highContrast = false,
this.disableAnimations = false,
this.boldText = false,
this.navigationMode = NavigationMode.traditional,
}) : assert(size != null),
assert(devicePixelRatio != null),
assert(textScaleFactor != null),
assert(platformBrightness != null),
assert(padding != null),
assert(viewInsets != null),
assert(systemGestureInsets != null),
assert(viewPadding != null),
assert(physicalDepth != null),
assert(alwaysUse24HourFormat != null),
assert(accessibleNavigation != null),
assert(invertColors != null),
assert(highContrast != null),
assert(disableAnimations != null),
assert(boldText != null),
assert(navigationMode != null);
/// Creates data for a media query based on the given window.
///
/// If you use this, you should ensure that you also register for
/// notifications so that you can update your [MediaQueryData] when the
/// window's metrics change. For example, see
/// [WidgetsBindingObserver.didChangeMetrics] or [Window.onMetricsChanged].
MediaQueryData.fromWindow(ui.Window window)
: size = window.physicalSize / window.devicePixelRatio,
devicePixelRatio = window.devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor = window.textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness = window.platformBrightness,
padding = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.padding, window.devicePixelRatio),
viewPadding = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.viewPadding, window.devicePixelRatio),
viewInsets = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.viewInsets, window.devicePixelRatio),
systemGestureInsets = EdgeInsets.fromWindowPadding(window.systemGestureInsets, window.devicePixelRatio),
physicalDepth = window.physicalDepth,
accessibleNavigation = window.accessibilityFeatures.accessibleNavigation,
invertColors = window.accessibilityFeatures.invertColors,
disableAnimations = window.accessibilityFeatures.disableAnimations,
boldText = window.accessibilityFeatures.boldText,
highContrast = window.accessibilityFeatures.highContrast,
alwaysUse24HourFormat = window.alwaysUse24HourFormat,
navigationMode = NavigationMode.traditional;
/// The size of the media in logical pixels (e.g, the size of the screen).
///
/// Logical pixels are roughly the same visual size across devices. Physical
/// pixels are the size of the actual hardware pixels on the device. The
/// number of physical pixels per logical pixel is described by the
/// [devicePixelRatio].
final Size size;
/// The number of device pixels for each logical pixel. This number might not
/// be a power of two. Indeed, it might not even be an integer. For example,
/// the Nexus 6 has a device pixel ratio of 3.5.
final double devicePixelRatio;
/// The number of font pixels for each logical pixel.
///
/// For example, if the text scale factor is 1.5, text will be 50% larger than
/// the specified font size.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.textScaleFactorOf], a convenience method which returns the
/// textScaleFactor defined for a [BuildContext].
final double textScaleFactor;
/// The current brightness mode of the host platform.
///
/// For example, starting in Android Pie, battery saver mode asks all apps to
/// render in a "dark mode".
///
/// Not all platforms necessarily support a concept of brightness mode. Those
/// platforms will report [Brightness.light] in this property.
final Brightness platformBrightness;
/// The parts of the display that are completely obscured by system UI,
/// typically by the device's keyboard.
///
/// When a mobile device's keyboard is visible `viewInsets.bottom`
/// corresponds to the top of the keyboard.
///
/// This value is independent of the [padding] and [viewPadding]. viewPadding
/// is measured from the edges of the [MediaQuery] widget's bounds. Padding is
/// calculated based on the viewPadding and viewInsets. The bounds of the top
/// level MediaQuery created by [WidgetsApp] are the same as the window
/// (often the mobile device screen) that contains the app.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ui.window], which provides some additional detail about this property
/// and how it relates to [padding] and [viewPadding].
final EdgeInsets viewInsets;
/// The parts of the display that are partially obscured by system UI,
/// typically by the hardware display "notches" or the system status bar.
///
/// If you consumed this padding (e.g. by building a widget that envelops or
/// accounts for this padding in its layout in such a way that children are
/// no longer exposed to this padding), you should remove this padding
/// for subsequent descendants in the widget tree by inserting a new
/// [MediaQuery] widget using the [MediaQuery.removePadding] factory.
///
/// Padding is derived from the values of [viewInsets] and [viewPadding].
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ui.window], which provides some additional detail about this
/// property and how it relates to [viewInsets] and [viewPadding].
/// * [SafeArea], a widget that consumes this padding with a [Padding] widget
/// and automatically removes it from the [MediaQuery] for its child.
final EdgeInsets padding;
/// The parts of the display that are partially obscured by system UI,
/// typically by the hardware display "notches" or the system status bar.
///
/// This value remains the same regardless of whether the system is reporting
/// other obstructions in the same physical area of the screen. For example, a
/// software keyboard on the bottom of the screen that may cover and consume
/// the same area that requires bottom padding will not affect this value.
///
/// This value is independent of the [padding] and [viewInsets]: their values
/// are measured from the edges of the [MediaQuery] widget's bounds. The
/// bounds of the top level MediaQuery created by [WidgetsApp] are the
/// same as the window that contains the app. On mobile devices, this will
/// typically be the full screen.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [ui.window], which provides some additional detail about this
/// property and how it relates to [padding] and [viewInsets].
final EdgeInsets viewPadding;
/// The areas along the edges of the display where the system consumes
/// certain input events and blocks delivery of those events to the app.
///
/// Starting with Android Q, simple swipe gestures that start within the
/// [systemGestureInsets] areas are used by the system for page navigation
/// and may not be delivered to the app. Taps and swipe gestures that begin
/// with a long-press are delivered to the app, but simple press-drag-release
/// swipe gestures which begin within the area defined by [systemGestureInsets]
/// may not be.
///
/// Apps should avoid locating gesture detectors within the system gesture
/// insets area. Apps should feel free to put visual elements within
/// this area.
///
/// This property is currently only expected to be set to a non-default value
/// on Android starting with version Q.
///
/// {@tool dartpad --template=stateful_widget_material}
///
/// For apps that might be deployed on Android Q devices with full gesture
/// navigation enabled, use [MediaQuery.systemGestureInsets] with [Padding]
/// to avoid having the left and right edges of the [Slider] from appearing
/// within the area reserved for system gesture navigation.
///
/// By default, [Slider]s expand to fill the available width. So, we pad the
/// left and right sides.
///
/// ```dart
/// double _currentValue = 0.2;
///
/// @override
/// Widget build(BuildContext context) {
/// EdgeInsets systemGestureInsets = MediaQuery.of(context).systemGestureInsets;
/// return Scaffold(
/// appBar: AppBar(title: Text('Pad Slider to avoid systemGestureInsets')),
/// body: Padding(
/// padding: EdgeInsets.only( // only left and right padding are needed here
/// left: systemGestureInsets.left,
/// right: systemGestureInsets.right,
/// ),
/// child: Slider(
/// value: _currentValue.toDouble(),
/// onChanged: (double newValue) {
/// setState(() {
/// _currentValue = newValue;
/// });
/// },
/// ),
/// ),
/// );
/// }
/// ```
/// {@end-tool}
final EdgeInsets systemGestureInsets;
/// The physical depth is the maximum elevation that the Window allows.
///
/// Physical layers drawn at or above this elevation will have their elevation
/// clamped to this value. This can happen if the physical layer itself has
/// an elevation larger than the available depth, or if some ancestor of the
/// layer causes it to have a cumulative elevation that is larger than the
/// available depth.
///
/// The default value is [double.maxFinite], which is used for platforms that
/// do not specify a maximum elevation. This property is currently only
/// expected to be set to a non-default value on Fuchsia.
final double physicalDepth;
/// Whether to use 24-hour format when formatting time.
///
/// The behavior of this flag is different across platforms:
///
/// - On Android this flag is reported directly from the user settings called
/// "Use 24-hour format". It applies to any locale used by the application,
/// whether it is the system-wide locale, or the custom locale set by the
/// application.
/// - On iOS this flag is set to true when the user setting called "24-Hour
/// Time" is set or the system-wide locale's default uses 24-hour
/// formatting.
final bool alwaysUse24HourFormat;
/// Whether the user is using an accessibility service like TalkBack or
/// VoiceOver to interact with the application.
///
/// When this setting is true, features such as timeouts should be disabled or
/// have minimum durations increased.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [Window.AccessibilityFeatures], where the setting originates.
final bool accessibleNavigation;
/// Whether the device is inverting the colors of the platform.
///
/// This flag is currently only updated on iOS devices.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [Window.AccessibilityFeatures], where the setting originates.
final bool invertColors;
/// Whether the user requested a high contrast between foreground and background
/// content on iOS, via Settings -> Accessibility -> Increase Contrast.
///
/// This flag is currently only updated on iOS devices that are running iOS 13
/// or above.
final bool highContrast;
/// Whether the platform is requesting that animations be disabled or reduced
/// as much as possible.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [Window.AccessibilityFeatures], where the setting originates.
final bool disableAnimations;
/// Whether the platform is requesting that text be drawn with a bold font
/// weight.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [Window.AccessibilityFeatures], where the setting originates.
final bool boldText;
/// Describes the navigation mode requested by the platform.
///
/// Some user interfaces are better navigated using a directional pad (DPAD)
/// or arrow keys, and for those interfaces, some widgets need to handle these
/// directional events differently. In order to know when to do that, these
/// widgets will look for the navigation mode in effect for their context.
///
/// For instance, in a television interface, [NavigationMode.directional]
/// should be set, so that directional navigation is used to navigate away
/// from a text field using the DPAD. In contrast, on a regular desktop
/// application with the `navigationMode` set to [NavigationMode.traditional],
/// the arrow keys are used to move the cursor instead of navigating away.
///
/// The [NavigationMode] values indicate the type of navigation to be used in
/// a widget subtree for those widgets sensitive to it.
final NavigationMode navigationMode;
/// The orientation of the media (e.g., whether the device is in landscape or
/// portrait mode).
Orientation get orientation {
return size.width > size.height ? Orientation.landscape : Orientation.portrait;
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given fields replaced
/// with the new values.
MediaQueryData copyWith({
Size size,
double devicePixelRatio,
double textScaleFactor,
Brightness platformBrightness,
EdgeInsets padding,
EdgeInsets viewPadding,
EdgeInsets viewInsets,
EdgeInsets systemGestureInsets,
double physicalDepth,
bool alwaysUse24HourFormat,
bool highContrast,
bool disableAnimations,
bool invertColors,
bool accessibleNavigation,
bool boldText,
NavigationMode navigationMode,
}) {
return MediaQueryData(
size: size ?? this.size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio ?? this.devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor ?? this.textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness ?? this.platformBrightness,
padding: padding ?? this.padding,
viewPadding: viewPadding ?? this.viewPadding,
viewInsets: viewInsets ?? this.viewInsets,
systemGestureInsets: systemGestureInsets ?? this.systemGestureInsets,
physicalDepth: physicalDepth ?? this.physicalDepth,
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat ?? this.alwaysUse24HourFormat,
invertColors: invertColors ?? this.invertColors,
highContrast: highContrast ?? this.highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations ?? this.disableAnimations,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation ?? this.accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText ?? this.boldText,
navigationMode: navigationMode ?? this.navigationMode,
);
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given [padding]s
/// replaced with zero.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then this
/// [MediaQueryData] is returned unmodified.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.removePadding], which uses this method to remove [padding]
/// from the ambient [MediaQuery].
/// * [SafeArea], which both removes the padding from the [MediaQuery] and
/// adds a [Padding] widget.
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [viewInsets].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for [viewPadding].
MediaQueryData removePadding({
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
}) {
if (!(removeLeft || removeTop || removeRight || removeBottom))
return this;
return MediaQueryData(
size: size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness,
padding: padding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
viewPadding: viewPadding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.left - padding.left) : null,
top: removeTop ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.top - padding.top) : null,
right: removeRight ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.right - padding.right) : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.bottom - padding.bottom) : null,
),
viewInsets: viewInsets,
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast: highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations,
invertColors: invertColors,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText,
);
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given [viewInsets]
/// replaced with zero.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then this
/// [MediaQueryData] is returned unmodified.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.removeViewInsets], which uses this method to remove
/// [viewInsets] from the ambient [MediaQuery].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [padding].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for [viewPadding].
MediaQueryData removeViewInsets({
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
}) {
if (!(removeLeft || removeTop || removeRight || removeBottom))
return this;
return MediaQueryData(
size: size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness,
padding: padding,
viewPadding: viewPadding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.left - viewInsets.left) : null,
top: removeTop ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.top - viewInsets.top) : null,
right: removeRight ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.right - viewInsets.right) : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? math.max(0.0, viewPadding.bottom - viewInsets.bottom) : null,
),
viewInsets: viewInsets.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast: highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations,
invertColors: invertColors,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText,
);
}
/// Creates a copy of this media query data but with the given [viewPadding]
/// replaced with zero.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then this
/// [MediaQueryData] is returned unmodified.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQuery.removeViewPadding], which uses this method to remove
/// [viewPadding] from the ambient [MediaQuery].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [padding].
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [viewInsets].
MediaQueryData removeViewPadding({
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
}) {
if (!(removeLeft || removeTop || removeRight || removeBottom))
return this;
return MediaQueryData(
size: size,
devicePixelRatio: devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor: textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness: platformBrightness,
padding: padding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
viewInsets: viewInsets,
viewPadding: viewPadding.copyWith(
left: removeLeft ? 0.0 : null,
top: removeTop ? 0.0 : null,
right: removeRight ? 0.0 : null,
bottom: removeBottom ? 0.0 : null,
),
alwaysUse24HourFormat: alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast: highContrast,
disableAnimations: disableAnimations,
invertColors: invertColors,
accessibleNavigation: accessibleNavigation,
boldText: boldText,
);
}
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) {
if (other.runtimeType != runtimeType)
return false;
return other is MediaQueryData
&& other.size == size
&& other.devicePixelRatio == devicePixelRatio
&& other.textScaleFactor == textScaleFactor
&& other.platformBrightness == platformBrightness
&& other.padding == padding
&& other.viewPadding == viewPadding
&& other.viewInsets == viewInsets
&& other.physicalDepth == physicalDepth
&& other.alwaysUse24HourFormat == alwaysUse24HourFormat
&& other.highContrast == highContrast
&& other.disableAnimations == disableAnimations
&& other.invertColors == invertColors
&& other.accessibleNavigation == accessibleNavigation
&& other.boldText == boldText
&& other.navigationMode == navigationMode;
}
@override
int get hashCode {
return hashValues(
size,
devicePixelRatio,
textScaleFactor,
platformBrightness,
padding,
viewPadding,
viewInsets,
physicalDepth,
alwaysUse24HourFormat,
highContrast,
disableAnimations,
invertColors,
accessibleNavigation,
boldText,
navigationMode,
);
}
@override
String toString() {
final List<String> properties = <String>[
'size: $size',
'devicePixelRatio: ${devicePixelRatio.toStringAsFixed(1)}',
'textScaleFactor: ${textScaleFactor.toStringAsFixed(1)}',
'platformBrightness: $platformBrightness',
'padding: $padding',
'viewPadding: $viewPadding',
'viewInsets: $viewInsets',
'physicalDepth: $physicalDepth',
'alwaysUse24HourFormat: $alwaysUse24HourFormat',
'accessibleNavigation: $accessibleNavigation',
'highContrast: $highContrast',
'disableAnimations: $disableAnimations',
'invertColors: $invertColors',
'boldText: $boldText',
'navigationMode: ${describeEnum(navigationMode)}',
];
return '${objectRuntimeType(this, 'MediaQueryData')}(${properties.join(', ')})';
}
}
/// Establishes a subtree in which media queries resolve to the given data.
///
/// For example, to learn the size of the current media (e.g., the window
/// containing your app), you can read the [MediaQueryData.size] property from
/// the [MediaQueryData] returned by [MediaQuery.of]:
/// `MediaQuery.of(context).size`.
///
/// Querying the current media using [MediaQuery.of] will cause your widget to
/// rebuild automatically whenever the [MediaQueryData] changes (e.g., if the
/// user rotates their device).
///
/// If no [MediaQuery] is in scope then the [MediaQuery.of] method will throw an
/// exception, unless the `nullOk` argument is set to true, in which case it
/// returns null.
///
/// {@youtube 560 315 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A3WrA4zAaPw}
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [WidgetsApp] and [MaterialApp], which introduce a [MediaQuery] and keep
/// it up to date with the current screen metrics as they change.
/// * [MediaQueryData], the data structure that represents the metrics.
class MediaQuery extends InheritedWidget {
/// Creates a widget that provides [MediaQueryData] to its descendants.
///
/// The [data] and [child] arguments must not be null.
const MediaQuery({
Key key,
@required this.data,
@required Widget child,
}) : assert(child != null),
assert(data != null),
super(key: key, child: child);
/// Creates a new [MediaQuery] that inherits from the ambient [MediaQuery]
/// from the given context, but removes the specified padding.
///
/// This should be inserted into the widget tree when the [MediaQuery] padding
/// is consumed by a widget in such a way that the padding is no longer
/// exposed to the widget's descendants or siblings.
///
/// The [context] argument is required, must not be null, and must have a
/// [MediaQuery] in scope.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then the returned
/// [MediaQuery] reuses the ambient [MediaQueryData] unmodified, which is not
/// particularly useful.
///
/// The [child] argument is required and must not be null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [SafeArea], which both removes the padding from the [MediaQuery] and
/// adds a [Padding] widget.
/// * [MediaQueryData.padding], the affected property of the
/// [MediaQueryData].
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.viewInsets].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for
/// [MediaQueryData.viewPadding].
factory MediaQuery.removePadding({
Key key,
@required BuildContext context,
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
@required Widget child,
}) {
return MediaQuery(
key: key,
data: MediaQuery.of(context).removePadding(
removeLeft: removeLeft,
removeTop: removeTop,
removeRight: removeRight,
removeBottom: removeBottom,
),
child: child,
);
}
/// Creates a new [MediaQuery] that inherits from the ambient [MediaQuery]
/// from the given context, but removes the specified view insets.
///
/// This should be inserted into the widget tree when the [MediaQuery] view
/// insets are consumed by a widget in such a way that the view insets are no
/// longer exposed to the widget's descendants or siblings.
///
/// The [context] argument is required, must not be null, and must have a
/// [MediaQuery] in scope.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then the returned
/// [MediaQuery] reuses the ambient [MediaQueryData] unmodified, which is not
/// particularly useful.
///
/// The [child] argument is required and must not be null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQueryData.viewInsets], the affected property of the
/// [MediaQueryData].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.padding].
/// * [removeViewPadding], the same thing but for
/// [MediaQueryData.viewPadding].
factory MediaQuery.removeViewInsets({
Key key,
@required BuildContext context,
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
@required Widget child,
}) {
return MediaQuery(
key: key,
data: MediaQuery.of(context).removeViewInsets(
removeLeft: removeLeft,
removeTop: removeTop,
removeRight: removeRight,
removeBottom: removeBottom,
),
child: child,
);
}
/// Creates a new [MediaQuery] that inherits from the ambient [MediaQuery]
/// from the given context, but removes the specified view padding.
///
/// This should be inserted into the widget tree when the [MediaQuery] view
/// padding is consumed by a widget in such a way that the view padding is no
/// longer exposed to the widget's descendants or siblings.
///
/// The [context] argument is required, must not be null, and must have a
/// [MediaQuery] in scope.
///
/// The `removeLeft`, `removeTop`, `removeRight`, and `removeBottom` arguments
/// must not be null. If all four are false (the default) then the returned
/// [MediaQuery] reuses the ambient [MediaQueryData] unmodified, which is not
/// particularly useful.
///
/// The [child] argument is required and must not be null.
///
/// See also:
///
/// * [MediaQueryData.viewPadding], the affected property of the
/// [MediaQueryData].
/// * [removePadding], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.padding].
/// * [removeViewInsets], the same thing but for [MediaQueryData.viewInsets].
factory MediaQuery.removeViewPadding({
Key key,
@required BuildContext context,
bool removeLeft = false,
bool removeTop = false,
bool removeRight = false,
bool removeBottom = false,
@required Widget child,
}) {
return MediaQuery(
key: key,
data: MediaQuery.of(context).removeViewPadding(
removeLeft: removeLeft,
removeTop: removeTop,
removeRight: removeRight,
removeBottom: removeBottom,
),
child: child,
);
}
/// Contains information about the current media.
///
/// For example, the [MediaQueryData.size] property contains the width and
/// height of the current window.
final MediaQueryData data;
/// The data from the closest instance of this class that encloses the given
/// context.
///
/// You can use this function to query the size an orientation of the screen.
/// When that information changes, your widget will be scheduled to be
/// rebuilt, keeping your widget up-to-date.
///
/// Typical usage is as follows:
///
/// ```dart
/// MediaQueryData media = MediaQuery.of(context);
/// ```
///
/// If there is no [MediaQuery] in scope, then this will throw an exception.
/// To return null if there is no [MediaQuery], then pass `nullOk: true`.
///
/// If you use this from a widget (e.g. in its build function), consider
/// calling [debugCheckHasMediaQuery].
static MediaQueryData of(BuildContext context, { bool nullOk = false }) {
assert(context != null);
assert(nullOk != null);
final MediaQuery query = context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<MediaQuery>();
if (query != null)
return query.data;
if (nullOk)
return null;
throw FlutterError.fromParts(<DiagnosticsNode>[
ErrorSummary('MediaQuery.of() called with a context that does not contain a MediaQuery.'),
ErrorDescription(
'No MediaQuery ancestor could be found starting from the context that was passed '
'to MediaQuery.of(). This can happen because you do not have a WidgetsApp or '
'MaterialApp widget (those widgets introduce a MediaQuery), or it can happen '
'if the context you use comes from a widget above those widgets.'
),
context.describeElement('The context used was')
]);
}
/// Returns textScaleFactor for the nearest MediaQuery ancestor or 1.0, if
/// no such ancestor exists.
static double textScaleFactorOf(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.of(context, nullOk: true)?.textScaleFactor ?? 1.0;
}
/// Returns platformBrightness for the nearest MediaQuery ancestor or
/// [Brightness.light], if no such ancestor exists.
///
/// Use of this method will cause the given [context] to rebuild any time that
/// any property of the ancestor [MediaQuery] changes.
static Brightness platformBrightnessOf(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.of(context, nullOk: true)?.platformBrightness ?? Brightness.light;
}
/// Returns the boldText accessibility setting for the nearest MediaQuery
/// ancestor, or false if no such ancestor exists.
static bool boldTextOverride(BuildContext context) {
return MediaQuery.of(context, nullOk: true)?.boldText ?? false;
}
@override
bool updateShouldNotify(MediaQuery oldWidget) => data != oldWidget.data;
@override
void debugFillProperties(DiagnosticPropertiesBuilder properties) {
super.debugFillProperties(properties);
properties.add(DiagnosticsProperty<MediaQueryData>('data', data, showName: false));
}
}
/// Describes the navigation mode to be set by a [MediaQuery] widget
///
/// The different modes indicate the type of navigation to be used in a widget
/// subtree for those widgets sensitive to it.
///
/// Use `MediaQuery.of(context).navigationMode` to determine the navigation mode
/// in effect for the given context. Use a [MediaQuery] widget to set the
/// navigation mode for its descendant widgets.
enum NavigationMode {
/// This indicates a traditional keyboard-and-mouse navigation modality.
///
/// This navigation mode is where the arrow keys can be used for secondary
/// modification operations, like moving sliders or cursors, and disabled
/// controls will lose focus and not be traversable.
traditional,
/// This indicates a directional-based navigation mode.
///
/// This navigation mode indicates that arrow keys should be reserved for
/// navigation operations, and secondary modifications operations, like moving
/// sliders or cursors, will use alternative bindings or be disabled.
///
/// Some behaviors are also affected by this mode. For instance, disabled
/// controls will retain focus when disabled, and will be able to receive
/// focus (although they remain disabled) when traversed.
directional,
}